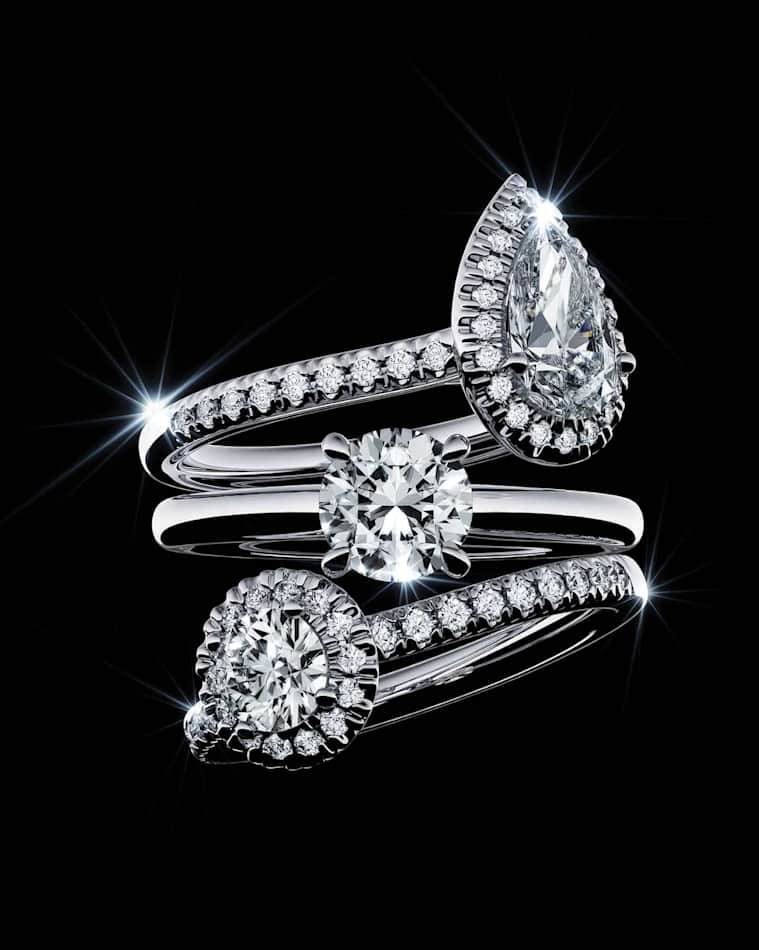
Que signifie 4C ?
Title:Clarté : principes et facteurs
Title:On jugera la clarté d’un diamant créé en laboratoire en fonction de ses défauts. Ce sont ses inclusions et ses imperfections qui lui prêtent un charme et un caractère uniques. Retrouvez ci-dessous plus d’informations sur la clarté du diamant.
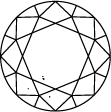
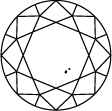
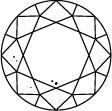



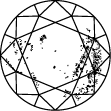

Schéma de clarté du diamant
Title:Échelle d’évaluation de la clarté du diamant
Subtitle:L’échelle de clarté du diamant s’étend de la note I.F à I 3, en fonction du nombre d’inclusions et d’impuretés de chaque pierre. Les degrés de pureté des diamants sont déterminés dans des conditions d'observation standardisées à l’aide d’une loupe de grossissement 10x. I.F. signifie que le diamant ne comporte aucun défaut interne. À l’inverse, I 3 correspond aux inclusions visibles. Les diamants dépourvus de tout défaut sont rarissimes. Presque toutes les pierres, y compris les diamants créés en laboratoire, contiennent des inclusions.
Taille : principes et facteurs
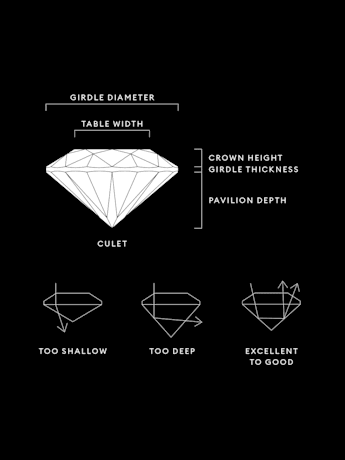
Title:La qualité d’un diamant créé en laboratoire dépend de ses proportions, de sa symétrie et de son polissage. La qualité de la taille créera une multitude de facettes afin que la lumière circule et se reflète sous tous ses angles.
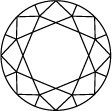
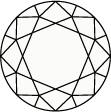
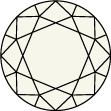

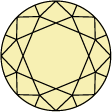
Schéma et échelle de graduation de la couleur du diamant
La couleur d’un diamant s’échelonne de D pour les couleurs d’un blanc pur à Z, pour les tonalités allant du jaune au brun. Chaque lettre correspond à une teinte, les lettres D à F étant attribuées aux tonalités incolores, et celles classées de S à Z, aux nuances jaune pâle ou brun.Les collections Swarovski sont créées à partir de diamants créés en laboratoire uniquement, et seules les pierres de qualité supérieure, dont la notation est comprise entre D et G (incolore à presque incolore), sont retenues.
Couleur : principes et facteurs
Title:Les pierres incolores sont les plus convoitées dans l’univers diamantaire, car elles sont d’une extrême rareté. Nos Swarovski Created Diamonds sont évalués en fonction d’une échelle de couleur standardisée.










Caratage
Title:Échelle de caratage de diamants créés en laboratoire
Subtitle:Le mot carat fait référence à la graine de caroubier appelée caroube. Les marchands l’utilisaient déjà comme unité de mesure du diamant dans l‘antiquité. Le carat est l’unité de mesure standard internationale désignée pour mesurer le poids du diamant. Un carat est équivalent à 200 milligrammes. Un diamant de 5 carats pèsera donc un gramme. Il ne se rapporte pas à la taille d’une pierre, mais uniquement à son poids, et déterminera la valeur marchande d’un diamant.
Tout savoir sur les Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Diamants créés en laboratoire
Subtitle:Découvrez l’univers des Swarovski Created Diamonds et ses superbes collections entre tradition et modernité. Des créations interstellaires d’une brillance extraordinaire à l’élégance naturelle de nos pièces emblématiques, trouvez le modèle qui vous accompagnera tout au long de votre vie.
Guide d’achat du diamant créé en laboratoire
Title:Trouvez la pièce parfaite
Subtitle:De nos valeurs, notre ADN et l’esprit créatif de notre marque nait naturellement une nouvelle collection de bijoux. Les Swarovski Created Diamonds sont des diamants créés en laboratoire grâce à notre unique savoir-faire, d’une brillance exceptionnelle. Identiques en tous points aux gemmes naturelles extraites des mines, seule leur provenance diffère. Formés, couche après couche, à partir d’un minuscule grain de carbone, ils sont le plus parfait reflet de l’éclat de la nature.
Qu’est-ce qu’un diamant créé en laboratoire ?
Title:Tous les secrets des diamants créés en laboratoire
Subtitle:Foire aux questions
Les 4C du diamant - FAQ
Que signifient les 4C ?
La clarté du diamant est-elle importante ?
Quel est le degré de clarté le plus élevé du diamant ?
Afin d’évaluer sa clarté, le diamant est inspecté à l’aide d’une loupe de grossissement 10x. Le nombre et la nature des éléments externes (imperfections) et internes (inclusions), ainsi que leur taille et leur position déterminent le degré de clarté.
Les pierres sont classées par les gemmologues de la meilleure note, IF (sans défaut interne), à la moins bonne, I3 (Inclusions).
Les diamants de laboratoire sont-ils sans défaut ?
Les diamants de laboratoire peuvent-ils perdre leur éclat ?
Comment se passe la certification et l’évaluation des diamants créés en laboratoire ?
Qu’appelle-t-on facette du diamant ?
De quelle manière définit-on la qualité de la taille ?
Quelle est la meilleure taille de diamant ?
Comment déterminer la couleur d’un diamant ?
Plus le diamant est incolore, meilleure sera jugée la qualité.