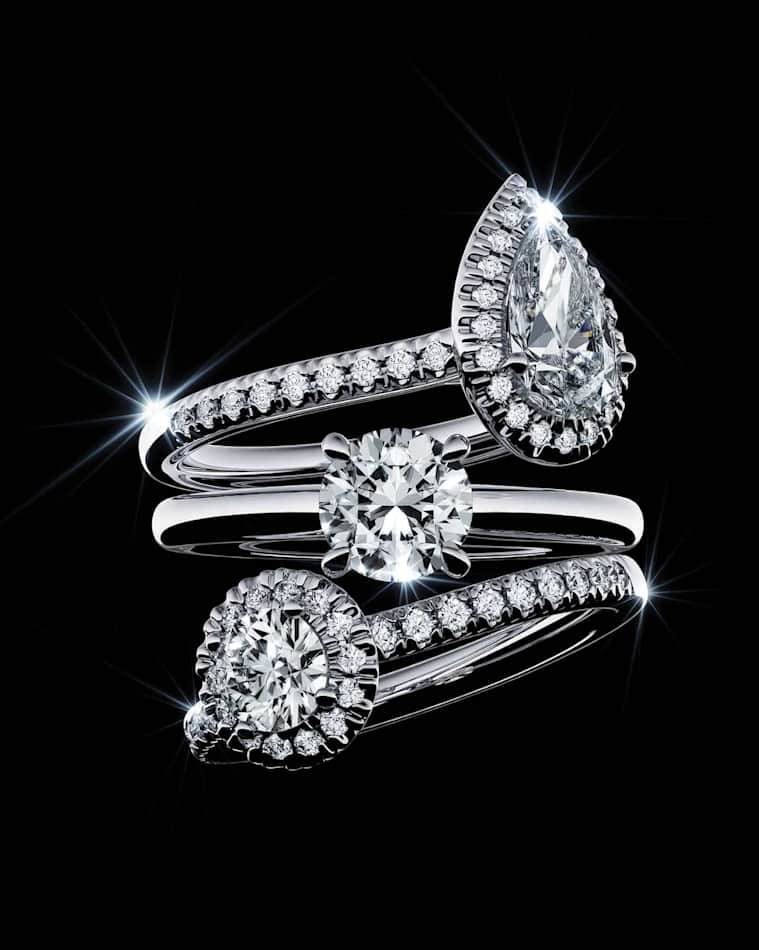
ダイヤモンドの4Cとは?
Title:ダイヤモンドの品質を評価する基準として全世界で使われている4Cは、ストーンの品質と価値を決定します。4Cとは、カラー、カット、カラット、そしてクラリティを指します。Swarovski Created Diamondsコレクションのラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドは、International Gemological Institute(IGI)の鑑定を受け、ダイヤモンドの4Cに準じてその品質が認証されており、カラーはG以上、クラリティはVS以上など、優れた品質が認められたラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドのみが使われることを許されます。
クラリティの原則と要素
Title:ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドのクラリティはインクルージョンやブレミッシュの有無や位置によって評価されますが、ダイヤモンドに独特の個性と魅力を与えてくれる要因でもあります。クラリティの詳細をご覧ください。
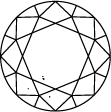
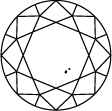
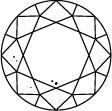



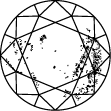

ダイヤモンドのクラリティを表すチャート
Title:ダイヤモンドのクラリティ・スケールとグレード
Subtitle:ダイヤモンドのクラリティ・スケールはIFからI3までに分かれており、ストーンの中に含まれるインクルージョンやブレミッシュの数や位置に基づいています。ダイヤモンドのクラリティのグレードは、標準条件における10倍拡大下で見えるインクルージョンで決定されます。IFは内部にインクルージョンが無いダイヤモンドを表しますが、クラリティ・スケールで反対の位置にあるI3は、インクルージョンやブレミッシュがはっきり見えることを示しています。真に欠陥のないダイヤモンドは非常に稀であり、ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドをはじめとするほとんどのストーンには、何らかのインクルージョンやブレミッシュが含まれています。
カットの原則と要素
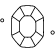
Title:ラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドのカットのグレードは、プロポーション、シンメトリー、ポリッシュの3つの要素に基づいて評価されます。高い技術者によるカットだからこそ、光を吸収して反射するファセットが数多く生まれ、ストーンがあらゆる角度からきらめきます。

ダイヤモンドのカラースケールとチャート
ダイヤモンドのカラーはDからZまでのスケールで評価され、Dは黄色味のない透明なアイスホワイトですが、Zは黄色や茶色の色合いです。チャートのアルファベットが示す範囲はストーンの色合いを示しており、DからFまでは無色、SからZまでは薄い黄色または茶色の色合いであることを意味しています。Swarovski Created Diamondsコレクションには、無色からほとんど無色(D~G)である最高級のラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドのみが使用されています。
カラーの原則と要素
Title:









ダイヤモンドのカラット
Title:ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドのカラット・スケール
Subtitle:カラットの語源は、古代の商人がダイヤモンドの重さを測る時の基準として使用していた「イナゴマメ(carob)」の種子に由来します。カラットは、ダイヤモンドの重さを測る国際標準計量単位です。1カラットは0.2gで、5カラットのダイヤモンドの重量は1gになります。ダイヤモンドのカラットはストーンの大きさではなく、単にその重さを指します。ダイヤモンドは通常、カラット数が大きくなるにつれ高価になります。
Swarovski Created Diamondsのすべて
Title:ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンド
Subtitle:伝統と最新のトレンドを融合した卓越した芸術性が表現され、ダイヤモンドの未来を再定義したSwarovski Created Diamondsコレクションの世界をご覧ください。まるで別世界のような輝きを放つ星々のコレクションから、純粋なエレガンスが感じられるシグネチャーアイテムまで、永遠に愛用したいスタイルが見つかります。
Leitfaden für im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten
Title:Finden Sie das perfekte Schmuckstück
Subtitle:Was sind im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten?
Title:Alles über im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten
Subtitle:Häufig gestellte Fragen
FAQ zum 4C-Qualitätssystem
Was sind die 4C?
Ist die Reinheit eines Diamanten wichtig?
Was ist der höchste Reinheitsgrad für Diamanten?
Zur Bewertung der Reinheit wird ein Diamant bei 10-facher Vergrößerung betrachtet. Die Anzahl und Natur von externen (Mängel) und internen Eigenschaften (Einschlüsse) sowie Größe und Position legen den Grad fest.
Gemmologen halten sich dabei an eine internationale Skala, angefangen bei Internally Flawless (I.F., makellos) als die höchste Qualitätsstufe, bis hin zu Included (I 3), das heißt mit Einschlüssen.
Sind im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten makellos?
Beschlagen im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten?
Wie werden gezüchtete Diamanten zertifiziert und eingestuft?
Was sind Diamantfacetten?
Wie wird die Diamantschliffqualität festgelegt?
Was ist der beste Diamantschliff?
Wie wird die Farbe eines Diamanten bestimmt?
Je mehr sich der Diamant der Stufe farblos nähert, desto höher ist die Qualität.