What Are the 4Cs of Diamonds?
Title:Clarity Principles and Factors
Title:
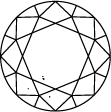
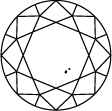
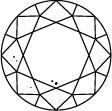



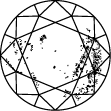

Diamond Clarity Chart
Title:Diamond clarity scale and grades
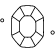
Subtitle:Cut Principles and Factors
Title:

Diamond color scale and chart
Diamond coloring is rated on a scale from D to Z, with D clear ice white with no hint of yellow, while those rated Z are shades of yellow and brown. Each letter range on the chart denotes a shade of stone, with those rated D to F appearing colorless, through to S to Z appearing in shades of light yellow or brown. Swarovski only accepts the finest laboratory grown diamonds in its collections, meaning they range from colorless to nearly colorless diamonds (D-G).
Color Principles and Factors
Title:









Diamond Carat Weight
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamond Carat Scale
Subtitle:All About Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds
Subtitle:Laboratory Grown Diamonds Buying Guide
Title:Find the perfect piece
Subtitle:What are Laboratory Grown Diamonds?
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds explained
Subtitle:Frequently asked questions
Diamond 4Cs FAQs
What are the 4Cs?
Is diamond clarity important?
What is the highest diamond clarity?
In order to assess clarity, the diamond is inspected under 10x power magnification. The number and nature of external (blemishes), and internal characteristics (inclusions), as well as their size and position, determine the grade.
Gemologists grade diamonds from Internally Flawless (IF) as the highest quality to Included (I3).
Are laboratory grown diamonds flawless?
Do laboratory grown diamonds get cloudy?
How are laboratory grown diamonds certified and graded?
What are diamond facets?
다이아몬드 파셋이란 다이아몬드의 모양을 만드는 각각의 평평한 표면을 뜻합니다. 모든 다이아몬드는 빛을 흡수하고 반사할 수 있도록 여러 파셋이 연출되어 있습니다.
다이아몬드의 컷 품질은 어떻게 결정되나요?
보통은 다이아몬드 컷을 모양(라운드, 하트, 오벌, 마퀴즈, 페어)으로 생각합니다. 하지만 다이아몬드 컷은 다이아몬드 파셋이 얼마나 빛과 아름답게 어우러지는가를 뜻합니다. 다이아몬드 컷은 다이아몬드의 모양, 기하학적 구조, 마감의 품질을 측정하는 하나의 척도입니다. 라운드 브릴리언트 다이아몬드는 Ideal(최고)부터 Poor(최하) 척도까지 정형화된 컷 등급을 받게 됩니다. Swarovski는 모든 랩그로운 다이아몬드가 최적의 빛 퍼포먼스와 반짝임을 선사할 수 있도록 컷 품질에 있어 어떠한 타협도 하지 않습니다.
최고의 다이아몬드 컷은 무엇인가요?
컷은 다이아몬드의 파셋이 빛에 반응하여 스톤 내부의 파이어를 드러내는 방식을 일컫는 표현입니다. 다이아몬드 각각에 고유한 개성을 불어넣는 컷과 랩그로운 다이아몬드의 완벽한 비율, 대칭성, 정밀 컷 앵글을 통해 Swarovski Created Diamonds는 누구도 비견할 수 없는 환상적인 광채로 빛납니다. 최고의 컷은 너비, 깊이 간의 균형이 절묘하게 맞아 너무 얇지도, 깊지도 않은 대칭 상태를 완성하는 것입니다. 다이아몬드를 투과하는 완벽한 빛의 굴절점을 만들면 다이아몬드가 내부에서부터 빛을 반사하여 눈부신 아름다움을 느낄 수 있죠.
다이아몬드의 컬러는 어떻게 결정되나요?
다이아몬드는 컬러리스에 가까울수록 높은 품질을 갖습니다.
랩그로운 다이아몬드는 흠집이 있나요?
저품질 다이아몬드 시드를 사용한 경우, 일부 랩그로운 다이아몬드는 내포물로 인한 컬러, 구조적 결함과 같은 명백한 결함이 발견될 수도 있습니다. Swarovski는 랩그로운 다이아몬드 가운데 자연스럽지 못하고 문제가 있는 다이아몬드를 판매하지 않습니다.
다이아몬드 캐럿 중량이란 무엇인가요?
캐럿이란 실험실에서 생산된 다이아몬드를 비롯하여 스톤을 측정하기 위해 별도로 사용하는 중량 단위에 해당합니다. 다이아몬드는 크기와 캐럿 중량이 비례하지 않을 수 있습니다. 같은 캐럿 중량의 다이아몬드라 할지라도 깊게 절단했을 때 사이즈가 달라질 수 있죠. 1캐럿의 중량은 1/5그램으로, 100포인트 단위로 나누어집니다.
다이아몬드 캐럿 중량은 무엇이며, 측정 방식과 이게 중요한 이유는 무엇인가요?
캐럿 중량이란 다이아몬드 표준 중량의 단위이며, 측정은 다이아몬드 등급 평가 과정에서 첫 번째로 이루어집니다. 다이아몬드 캐럿 중량은 다이아몬드의 중량을 측정한 값입니다. 각 캐럿은 100 “포인트” 단위로 세분화됩니다. 소수점 100자리까지 정밀하게 측정이 이루어지죠. 1캐럿 이하의 소형 다이아몬드 중량은 “포인트” 만으로 설명이 이루어집니다. 다이아몬드가 크면 클수록 캐럿 역시 값이 높아지지만 그 중요성은 오직 사용자의 평가에 의해서만 가치가 결정됩니다.