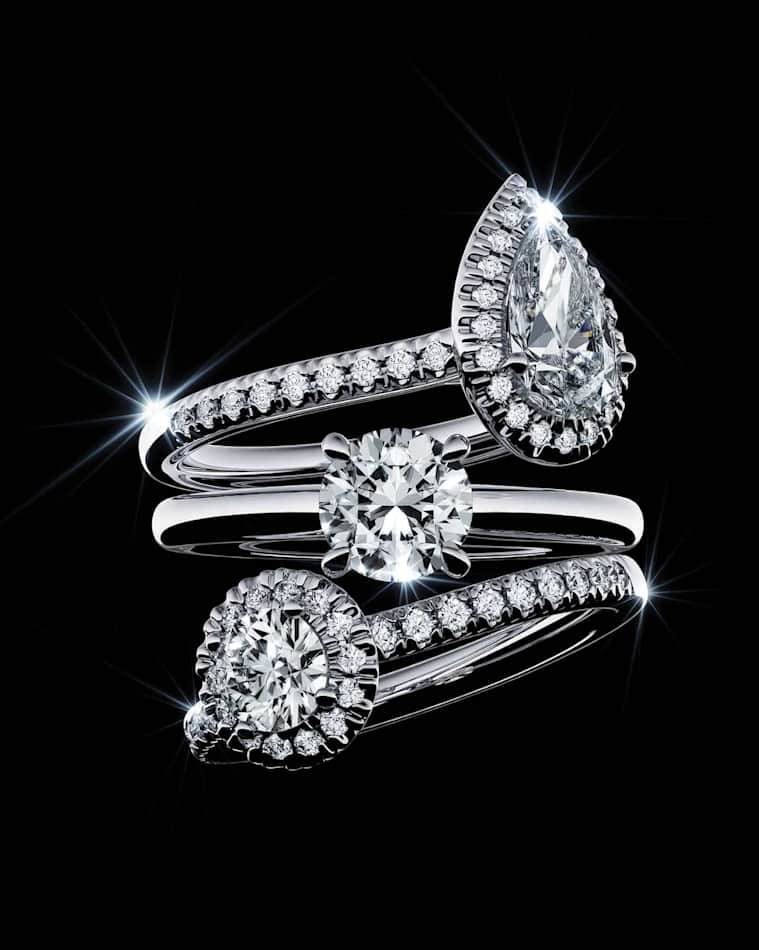
Que signifie 4C ?
Title:Clarté : principes et facteurs
Title:On jugera la clarté d’un diamant créé en laboratoire en fonction de ses défauts. Ce sont ses inclusions et ses imperfections qui lui prêtent un charme et un caractère uniques. Retrouvez ci-dessous plus d’informations sur la clarté du diamant.
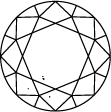
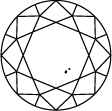
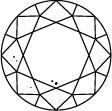



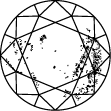

Schéma de clarté du diamant
Title:Échelle d’évaluation de la clarté du diamant
Subtitle:L’échelle de clarté du diamant s’étend de la note I.F à I 3, en fonction du nombre d’inclusions et d’impuretés de chaque pierre. Les degrés de pureté des diamants sont déterminés dans des conditions d'observation standardisées à l’aide d’une loupe de grossissement 10x. I.F. signifie que le diamant ne comporte aucun défaut interne. À l’inverse, I 3 correspond aux inclusions visibles. Les diamants dépourvus de tout défaut sont rarissimes. Presque toutes les pierres, y compris les diamants créés en laboratoire, contiennent des inclusions.
Taille : principes et facteurs
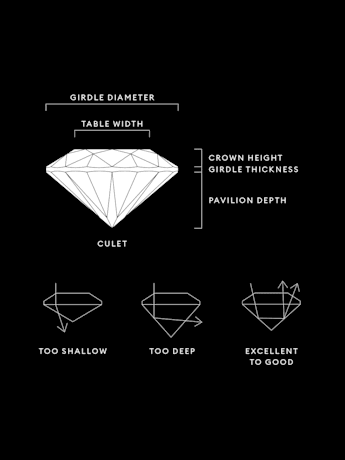
Title:La qualité d’un diamant créé en laboratoire dépend de ses proportions, de sa symétrie et de son polissage. La qualité de la taille créera une multitude de facettes afin que la lumière circule et se reflète sous tous ses angles.
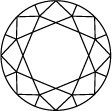
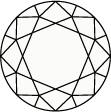
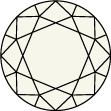

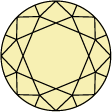
Schéma et échelle de graduation de la couleur du diamant
La couleur d’un diamant s’échelonne de D pour les couleurs d’un blanc pur à Z, pour les tonalités allant du jaune au brun. Chaque lettre correspond à une teinte, les lettres D à F étant attribuées aux tonalités incolores, et celles classées de S à Z, aux nuances jaune pâle ou brun.Les collections Swarovski sont créées à partir de diamants créés en laboratoire uniquement, et seules les pierres de qualité supérieure, dont la notation est comprise entre D et G (incolore à presque incolore), sont retenues.
Couleur : principes et facteurs
Title:Les pierres incolores sont les plus convoitées dans l’univers diamantaire, car elles sont d’une extrême rareté. Nos Swarovski Created Diamonds sont évalués en fonction d’une échelle de couleur standardisée.










Diamond Carat Weight
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamond Carat Scale
Subtitle:All About Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds
Subtitle:Laboratory Grown Diamonds Buying Guide
Title:Find the perfect piece
Subtitle:What are Laboratory Grown Diamonds?
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds explained
Subtitle:Frequently asked questions
Diamond 4Cs FAQs
What are the 4Cs?
Is diamond clarity important?
What is the highest diamond clarity?
In order to assess clarity, the diamond is inspected under 10x power magnification. The number and nature of external (blemishes), and internal characteristics (inclusions), as well as their size and position, determine the grade.
Gemologists grade diamonds from Internally Flawless (IF) as the highest quality to Included (I3).
Are laboratory grown diamonds flawless?
Do laboratory grown diamonds get cloudy?
How are laboratory grown diamonds certified and graded?
What are diamond facets?
How is diamond cut quality determined?
What is the best diamond cut?
How is a diamond’s color determined?
The closer the diamond is to being colorless, the higher its quality.