What Are the 4Cs of Diamonds?
Title:
Universally recognized, the 4Cs are a guiding light in the world of diamonds, helping to determine the quality and value of each stone - the 4Cs stand for color, cut, carat, and clarity. The laboratory grown diamonds in the Swarovski Created Diamonds collections are graded against these 4Cs by IGI, the International Gemological Institute. The laboratory grown diamonds in these collections are of very fine quality: G+ in color and VS+ in clarity.
Clarity Principles and Factors
Title:
The clarity of a laboratory grown diamond is judged by its flaws, which means the inclusions and blemishes that give it unique character and charm. Discover more about diamond clarity below.
I.F.
Internally flawless
VVS 1
VVS 2
Very very slightly included
VS 1
VS 2
Very slightly included
SI 1

SI 2

Slightly included
I 1

I 2
I 3

Included
Diamond Clarity Chart
Title:Diamond clarity scale and grades
Υπότιτλος:
The diamond clarity scale runs from I.F. to I 3 and is based on the number of inclusions and blemishes found in each stone. Diamond clarity grades are determined under standard viewing conditions with 10x magnification; I.F. is used to represent an internally flawless diamond, while at the other end of the diamond clarity chart, I 3 stands for the inclusion of a visible blemish. Truly flawless diamonds are extremely rare – almost all stones, including laboratory grown diamonds, have inclusions of some kind or other.
Cut Principles and Factors
Title:
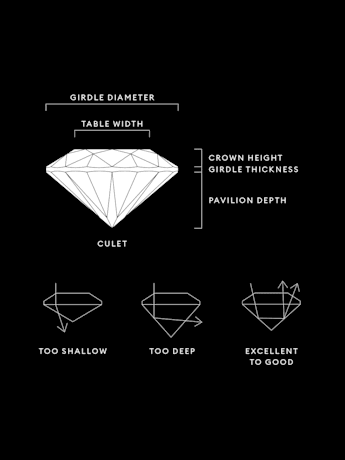
The quality of how a laboratory grown diamond is cut is based on its proportions, symmetry, and polish. An expert cut creates a multitude of facets, absorbing and reflecting the light so the stone shimmers from every angle.
Hochfeines Weiß
D–F
Feines Weiß
G–J
Leicht getöntes Weiß
K–M
Schwach gelblich

N–R
Schwach Gelb
S–Z
Farbskala für Diamanten
Die Farbe eines Diamanten wird auf einer Skala von D bis Z bewertet, wobei D für Clear Ice White (hochfeines Weiß) steht, ohne Gelbstich und Z für Gelb- und Brauntöne (getöntes Weiß). Die einzelnen Buchstaben der Skala bezeichnen Farbtöne, wobei D bis F farblos sind, bis hin zu S und Z, die für hellgelbe oder braune Farbtöne stehen. Für seine Kollektionen akzeptiert Swarovski nur die feinsten im Labor gezüchteten Diamanten, das heißt, sie befinden sich in der Palette von Farblos bis Fast farblos (D–G).
Farbprinzipien und Faktoren
Title:
Farblose Steine sind die begehrtesten in der Welt der Diamanten, da sie sehr selten sind. Die Diamanten der Swarovski Created Diamonds Kollektion werden basierend auf der Standard-Farbskala für Diamanten bewertet.

2,5 mm
0,05 CT

3,0 mm
0,10 CT

3,8 mm
0,20 CT

4,5 mm
0,30 CT

4,8 mm
0,40 CT

5,2 mm
0,50 CT

5,8 mm
0,70 CT

6,3 mm
0,90 CT

6,5 mm
1,00 CT

6,9 mm
1,25 CT
7,4 mm
1,50 CT
7,8 mm
1,75 CT
8,2 mm
2,00 CT
8,8 mm
2,50 CT
9,4 mm
3,00 CT
Karatgewicht eines Diamanten
Title:Karatskala für im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten
Υπότιτλος:
Die Messung in Karat stammt vom Wort „Carob“, dem Johannisbrotbaumsamen, den die Händler der Alten Welt ursprünglich als Referenz zum Erfassen des Gewichts eines Diamanten verwendeten. Karat ist ein internationaler Messstandard für die Erfassung des Gewichts eines Diamanten. Ein Karat entspricht 200 Milligramm, das heißt, ein 5-karätiger Diamant wiegt ein Gramm. Die Karatzahl eines Diamanten bezieht sich jedoch nicht auf seine Größe, sondern lediglich auf sein Gewicht. Normalerweise steigt der Wert eines Diamanten mit zunehmenden Karat.
Entdecken Sie Swarovski Created Diamonds
Alles über Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten
Υπότιτλος:
Entdecken Sie die Welt der Swarovski Created Diamonds Schmuckstücke, welche die Zukunft der Diamanten mit außergewöhnlichen Kollektionen, die Tradition und aktuelle Trends vereinen, neu definiert. Angefangen bei unglaublich brillantem Glanz bis hin zu unserer galaktischen Kollektion und der reinen Eleganz unserer Signature-Pieces. Finden Sie einen Style, der Sie ein Leben lang begleiten wird.
Leitfaden für im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten
Title:Finden Sie das perfekte Schmuckstück
Υπότιτλος:
Die Swarovski Created Diamonds Schmuckkollektion ist eine natürliche Weiterentwicklung unserer Marken-DNA. Die im Labor gezüchteten Diamanten sind meisterhaft geschliffen, intensiv leuchtend und in jeder Hinsicht identisch mit ihren im Bergbau geförderten Gegenstücken – mit Ausnahme ihrer Herkunft Sie wachsen Schicht für Schicht um einen Kohlenstoffkeim und sind ein makelloses Spiegelbild der Strahlkraft der Natur.
Was sind im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten?
Title:Alles über im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten
Υπότιτλος:
Erfahren Sie mehr über im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten und wie es gelingt, den natürlichen Wachstumsprozess in der Erde optimal nachzuahmen. Entdecken Sie die unterschiedlichen Diamantschliffe, die in den Swarovski Created Diamonds Kollektionen zum Einsatz kommen, sowie die Inspirationen hinter den Designs.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
FAQ zum 4C-Qualitätssystem
Was sind die 4C?
Jeder Diamant ist anders und hat seine ganz besonderen, unverkennbaren Merkmale. Im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten sind zu 100 % Diamanten und werden genau wie abgebaute Diamanten basierend auf dem 4C-Bewertungssystem eingestuft. Bei den 4C handelt es sich um Farbe (color), Reinheit (clarity), Schliff (cut), Karat (carat). Dieser internationale Standard wird für die Einstufung der Qualität von Diamanten eingesetzt.
Ist die Reinheit eines Diamanten wichtig?
Je höher die Einstufung, desto weniger Einschlüsse oder Mängel hat ein Diamant, was ihn zu einem hochwertigeren Edelstein macht als einen Diamanten mit einer niedrigeren Einstufung.
Was ist der höchste Reinheitsgrad für Diamanten?
Die Reinheit eines Diamanten wird basierend auf der Klarheit des Steins bewertet, wobei zwei Kriterien betrachtet werden: Einschlüsse und Fehler.
Zur Bewertung der Reinheit wird ein Diamant bei 10-facher Vergrößerung betrachtet. Die Anzahl und Natur von externen (Mängel) und internen Eigenschaften (Einschlüsse) sowie Größe und Position legen den Grad fest.
Gemmologen halten sich dabei an eine internationale Skala, angefangen bei Internally Flawless (I.F., makellos) als die höchste Qualitätsstufe, bis hin zu Included (I 3), das heißt mit Einschlüssen.
Zur Bewertung der Reinheit wird ein Diamant bei 10-facher Vergrößerung betrachtet. Die Anzahl und Natur von externen (Mängel) und internen Eigenschaften (Einschlüsse) sowie Größe und Position legen den Grad fest.
Gemmologen halten sich dabei an eine internationale Skala, angefangen bei Internally Flawless (I.F., makellos) als die höchste Qualitätsstufe, bis hin zu Included (I 3), das heißt mit Einschlüssen.
Sind im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten makellos?
Nein, fast alle Diamanten (abgebaute und im Labor gezüchtete) weisen Einschlüsse auf. Bei im Labor gezüchteten Diamanten kann es zu metallischen Einschlüssen kommen. Wenn ein Experte in einem Diamanten eine Spur von Metall erkennt, kann er davon ausgehen, dass dieser im Labor gezüchtet wurde. Obwohl auch im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten Mängel aufweisen können, verwendet Swarovski ausschließlich solche mit einer hohen Qualität, die vom International Gemological Institute (IGI) basierend auf dem 4C-System zertifiziert wurden. So stellen wir sicher, dass nur die hochwertigsten Diamanten für die Swarovski Created Diamonds Kollektionen verarbeitet werden.
Beschlagen im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten?
Nein, im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten beschlagen nicht im Laufe der Zeit. Sie gleichen zu 100 % natürlichen Diamanten, weisen dieselben physikalischen und chemischen Eigenschaften auf und sollten somit im Laufe der Zeit nicht degradieren oder ihr Aussehen verändern. Wenn minderwertige Diamantkeime verwendet wurden, können im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten offensichtliche Fehler aufweisen, wie Verfärbungen von Unreinheiten im Diamanten oder Makel in der kristallinen Struktur. Die für die Swarovski Created Diamonds Schmuckstücke verarbeiteten im Labor gezüchteten Diamanten weisen eine sehr hohe Qualität auf und haben keine unnatürlichen, problematischen Charakteristika.
Wie werden gezüchtete Diamanten zertifiziert und eingestuft?
Die im Labor gezüchteten Diamanten, die in den Swarovski Created Diamonds Schmuckstücken verarbeitet werden, sind handverlesen und von erfahrenen Gemmologen untersucht, um sicherzustellen, dass sie unsere hohen Qualitätsstandards erfüllen. Jedes einzelne Schmuckstück der Kollektionen Galaxy und Eternity wird von einem digitalen Laborbericht des International Gemological Institute (IGI) begleitet.
Was sind Diamantfacetten?
Diamantfacetten bezeichnen die ebenen Oberflächen, welche die Form des Diamanten bilden. Jeder Diamant hat zahlreiche Facetten, die es ihm ermöglichen, Licht zu absorbieren und zu reflektieren.
Wie wird die Diamantschliffqualität festgelegt?
Häufig stellen wir uns einen Diamantschliff als Form vor (rund, herzförmig, oval, Marquise, Tropfen). In Wirklichkeit bezeichnet Diamantschliff jedoch, wie gut die Facetten des Diamanten mit Licht interagieren. Der Schliff eines Diamanten ergibt die Qualität die Form, Geometrie und die Verarbeitung des Diamanten. Runde brillante Diamanten werden auf einer offiziellen Schliffskala bewertet, angefangen bei ideal (beste Stufe) bis hin zu schlecht. Swarovski macht keine Abstriche in Sachen Schliffqualität. Dies versichert, dass all unsere im Labor gezüchteten Diamanten eine optimale Lichtperformance und Brillanz aufweisen.
Was ist der beste Diamantschliff?
Der Schliff bezieht sich auf die Interaktion der verschiedenen Facetten eines Diamanten mit Licht, um sein inneres Feuer zu entfachen. Der Schliff verleiht jedem Diamanten seine einzigartige Persönlichkeit. Er optimiert die Proportionen, die Symmetrie und die Präzision des Schliffs von im Labor gezüchteten Diamanten und verleiht den Swarovski Created Diamonds ihre Brillanz. Der beste Schliff ist das optimale Gleichgewicht aus Breite und Tiefe, sodass Symmetrie entsteht, er ist weder zu flach noch zu tief. Es wird ein optimaler Brennpunkt für das Licht geschaffen, sodass dieses innerhalb des Diamanten reflektiert wird und seine polierte Strahlkraft unterstreicht.
Wie wird die Farbe eines Diamanten bestimmt?
Farbe bezeichnet bei weißen Diamanten den natürlichen Farbton. Der Branchenstandard für die Einstufung der Farbe wird verwendet, um jeden Diamanten basierend auf einer Referenzskala zu bewerten, um ihm anschließend einen Buchstaben von D (farblos) bis Z (hellgelb) zuzuweisen.
Je mehr sich der Diamant der Stufe farblos nähert, desto höher ist die Qualität.
Je mehr sich der Diamant der Stufe farblos nähert, desto höher ist die Qualität.
Weisen im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten Mängel auf?
Wurden minderwertige Diamantkeime verwendet, dann weisen manche im Labor gezüchteten Diamanten offensichtliche Mängel auf, wie Farbbeeinträchtigungen durch Unreinheiten oder strukturelle Fehler. Swarovski verkauft keine im Labor gezüchteten Diamanten mit unnatürlichen, problematischen Eigenschaften.
Was ist das Karatgewicht eines Diamanten?
Ein Karat ist eine Gewichtseinheit, die speziell dafür verwendet wird, um Edelsteine einzustufen, dies gilt auch für im Labor gezüchtete Diamanten. Ein Diamant kann ein höheres Karatgewicht haben, ohne größer als ein anderer mit einem geringeren Karatgewicht auszusehen. Zwei Diamanten mit demselben Karatgewicht können unterschiedlich groß sein, wenn einer davon tiefer geschliffen ist. Ein Karat wiegt 1/5 eines Gramms und wird in 100 Punkte aufgeteilt.
Was ist das Karatgewicht, wie wird es erfasst und wie wichtig ist es?
Das Karatgewicht ist die Standard-Gewichtseinheit für Diamanten und ist der erste Schritt des Evaluierungsverfahrens. Das Karatgewicht eines Diamanten gibt an, wie viel ein Diamant wiegt. Jedes Karat kann in 100 „Punkte“ unterteilt werden. Dies ermöglicht eine genaue Erfassung bis auf Hundertstel. Ein Diamant, der weniger wiegt als ein Karat, kann ausschließlich mit „Punkten“ eingestuft werden. Je größer ein Diamant ist, desto mehr Karat weist er in der Regel auf, doch nur Sie können entscheiden, wie wichtig Ihnen dieser Aspekt ist.
Ist ein hochkarätiger Diamant besser?
Das ist eine sehr persönliche Frage. Wenn Sie auf der Suche nach einem größeren Diamanten sind, dann sollten nach mehr Karat Ausschau halten, denn dies ist ein Hinweis auf das Gewicht und somit auf die Größe des Diamanten.