What Are the 4Cs of Diamonds?
Title:
Universally recognized, the 4Cs are a guiding light in the world of diamonds, helping to determine the quality and value of each stone - the 4Cs stand for color, cut, carat, and clarity. The laboratory grown diamonds in the Swarovski Created Diamonds collections are graded against these 4Cs by IGI, the International Gemological Institute. The laboratory grown diamonds in these collections are of very fine quality: G+ in color and VS+ in clarity.
Clarity Principles and Factors
Title:
The clarity of a laboratory grown diamond is judged by its flaws, which means the inclusions and blemishes that give it unique character and charm. Discover more about diamond clarity below.
I.F.
Internally flawless
VVS 1
VVS 2
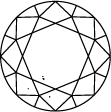
Very very slightly included
VS 1
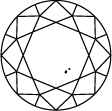
VS 2
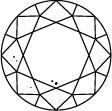
Very slightly included
SI 1

SI 2

Slightly included
I 1

I 2
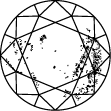
I 3

Included
Diamond Clarity Chart
Title:Diamond clarity scale and grades
Subtitle:
The diamond clarity scale runs from I.F. to I 3 and is based on the number of inclusions and blemishes found in each stone. Diamond clarity grades are determined under standard viewing conditions with 10x magnification; I.F. is used to represent an internally flawless diamond, while at the other end of the diamond clarity chart, I 3 stands for the inclusion of a visible blemish. Truly flawless diamonds are extremely rare – almost all stones, including laboratory grown diamonds, have inclusions of some kind or other.
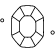
Cut Principles and Factors
Title:
The quality of how a laboratory grown diamond is cut is based on its proportions, symmetry, and polish. An expert cut creates a multitude of facets, absorbing and reflecting the light so the stone shimmers from every angle.
Colorless
D-F
Near colorless
G-J
Slightly tinted
K-M
Very light color

N-R
Light color
S-Z
Diamond color scale and chart
Diamond coloring is rated on a scale from D to Z, with D clear ice white with no hint of yellow, while those rated Z are shades of yellow and brown. Each letter range on the chart denotes a shade of stone, with those rated D to F appearing colorless, through to S to Z appearing in shades of light yellow or brown. Swarovski only accepts the finest laboratory grown diamonds in its collections, meaning they range from colorless to nearly colorless diamonds (D-G).
Color Principles and Factors
Title:
Colorless stones are the most desirable in the world of diamonds and they are extremely rare. Swarovski Created Diamonds are evaluated against the standardized diamond color scale.

2.5 mm
0.05 CT

3.0 mm
0.10 CT

3.8 mm
0.20 CT

4.5 mm
0.30 CT

4.8 mm
0.40 CT

5.2 mm
0.50 CT

5.8 mm
0.70 CT

6.3 mm
0.90 CT

6.5 mm
1.00 CT

6.9 mm
1.25 CT
7.4 mm
1.50 CT
7.8 mm
1.75 CT
8.2 mm
2.00 CT
8.8 mm
2.50 CT
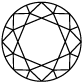
9.4 mm
3.00 CT
Diamond Carat Weight
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamond Carat Scale
Subtitle:
The carat measurement is derived by the word ‘carob’, a seed that was used as a diamond weight reference for traders in the ancient world. Carats are an international standard unit of measurement for the weight of a diamond. One carat is equal to 200 milligrams, so a 5 carat diamond will weigh one gram. The diamond carat does not refer to the size of a stone, simply how much it weighs. Diamonds usually become more expensive as their carat increases.
Discover Swarovski Created Diamonds
All About Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds
Subtitle:
Discover the world of Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry, redefining the future of diamonds with exceptional collections that bridge the gap between tradition and current trends. From the otherworldly brilliance of our interstellar collection to the pure elegance of our signature pieces, find a style that will last a lifetime.
Laboratory Grown Diamonds Buying Guide
Title:Find the perfect piece
Subtitle:
A natural progression of our brand DNA, Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry are laboratory grown diamonds, masterfully cut, intensely bright, and identical to their mined counterparts in every way but origin. Formed layer by layer from a carbon seed, they serve as a flawless reflection of nature’s radiance.
What are Laboratory Grown Diamonds?
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds explained
Subtitle:
Find out more about diamonds that are grown in a laboratory, and how the process of replicating the way diamonds are formed in the earth is achieved. Discover the different cuts of diamonds in the Swarovski Created Diamond Collections, as well as the inspiration behind the designs.
Frequently asked questions
Diamond 4Cs FAQs
What are the 4Cs?
Every diamond varies slightly from the next and has its own individual distinguishing characteristics. Laboratory grown diamonds are 100% diamonds, and just like mined diamonds our laboratory grown diamonds are evaluated according to the 4Cs of diamond grading. The 4Cs are color, clarity, cut and carat weight, and they are the globally accepted standards used to assess the quality of diamonds.
Is diamond clarity important?
The higher the clarity grading, the less inclusions or blemishes a diamond has, making it a higher-value diamond than one with a lower grading.
What is the highest diamond clarity?
Diamond clarity is a measure of the purity of the stone graded by the visibility of two types of characteristics - inclusions and blemishes.
In order to assess clarity, the diamond is inspected under 10x power magnification. The number and nature of external (blemishes), and internal characteristics (inclusions), as well as their size and position, determine the grade.
Gemologists grade diamonds from Internally Flawless (IF) as the highest quality to Included (I3).
In order to assess clarity, the diamond is inspected under 10x power magnification. The number and nature of external (blemishes), and internal characteristics (inclusions), as well as their size and position, determine the grade.
Gemologists grade diamonds from Internally Flawless (IF) as the highest quality to Included (I3).
Are laboratory grown diamonds flawless?
No, nearly all diamonds (mined or laboratory grown) have inclusions. Metallic inclusions can occur in laboratory grown diamonds. If an expert spots a trace of metal in a diamond, they can assume it is laboratory grown. While laboratory grown diamonds with defects do exist, Swarovski only uses high quality laboratory grown diamonds certified by the International Gemological Institute (IGI) according to the 4Cs to ensure that only the finest quality diamonds join the Swarovski Created Diamond collections.
Do laboratory grown diamonds get cloudy?
No, laboratory-grown diamonds do not get cloudy over time. They are 100% identical to diamonds with the same physical and chemical properties, and should not degrade or change appearance over time. Where poor quality diamond seeds have been used, some laboratory-grown diamonds contain obvious defects, such as color tinges from impurities in the diamond or crystal structure imperfections. The laboratory grown diamonds processed in Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry are a very high quality standard and do not have unnatural, problematic characteristics.
How are laboratory grown diamonds certified and graded?
The laboratory grown diamonds processed in Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry are hand-selected and examined by experienced gemologists to ensure they fulfill our high quality standards. Every piece of jewelry in the Galaxy and Eternity collections is accompanied with a digital laboratory report from the International Gemological Institute (IGI).
What are diamond facets?
Diamond facets refer to each flat surface that creates the shape of a diamond. Every diamond possesses multiple facets that enable it to absorb and reflect light.
How is diamond cut quality determined?
We often think of a diamond’s cut as shape (round, heart, oval, marquise, pear), but what diamond cut actually does mean is how well a diamond’s facets interact with light. The cut of a diamond is the measure of the quality of the shape, geometry and finish of the diamond. Round brilliant diamonds receive a formal cut grade on a scale from Ideal (the best) to Poor. Swarovski is uncompromising on cut quality to ensure all of our laboratory grown diamonds have optimal light performance and sparkle.
What is the best diamond cut?
Cut refers to how a diamond’s facets interact with light to reveal its internal fire. It is the cut that gives each diamond its personality, and perfecting laboratory grown diamonds proportions, symmetry, and precision-cut angles of Swarovski Created Diamonds gives them their brilliant shine. The best cut has a balance between the width and depth to create symmetry, neither to shallow nor to deep. Creating the perfect refraction point for light through the diamond, reflecting it within the diamond and highlighting its polished brightness.
How is a diamond’s color determined?
Color refers to the natural tint inherent in white diamonds. The industry standard for grading color is to evaluate each diamond against a master set then assign a letter grade from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow).
The closer the diamond is to being colorless, the higher its quality.
The closer the diamond is to being colorless, the higher its quality.
Do laboratory created diamonds have blemishes?
Where poor quality diamond seeds have been used, some laboratory-grown diamonds contain obvious defects, such as color tinges from impurities or structural imperfections. Swarovski does not sell laboratory grown diamonds with unnatural, problematic characteristics.
What is diamond carat weight?
A carat is a unit of weight used specifically to measure precious stones including laboratory grown diamonds. A diamond may have a higher carat weight without appearing larger, and two diamonds of the same carat weight can vary in size if one is cut deeper than the other. One carat weighs 1/5 of a gram and is divided into 100 points.
What is the carat weight of a diamond, how is it measured and how important is it?
Carat weight it the standard weight unit for diamonds, and the first step in the grading process. Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much the diamond weighs. Each carat can be subdivided into 100 “points.” This allows precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place. The weight of a diamond smaller than one carat may be described by its “points” alone. The larger the diamond is, the more carats it will be, but only you can decide how important that is to you.
Is it better to have a higher carat diamond?
This is an entirely personal question. If you are looking for a larger diamond, you should look for a higher carat, as this indicates the weight and therefore the size of the diamond.