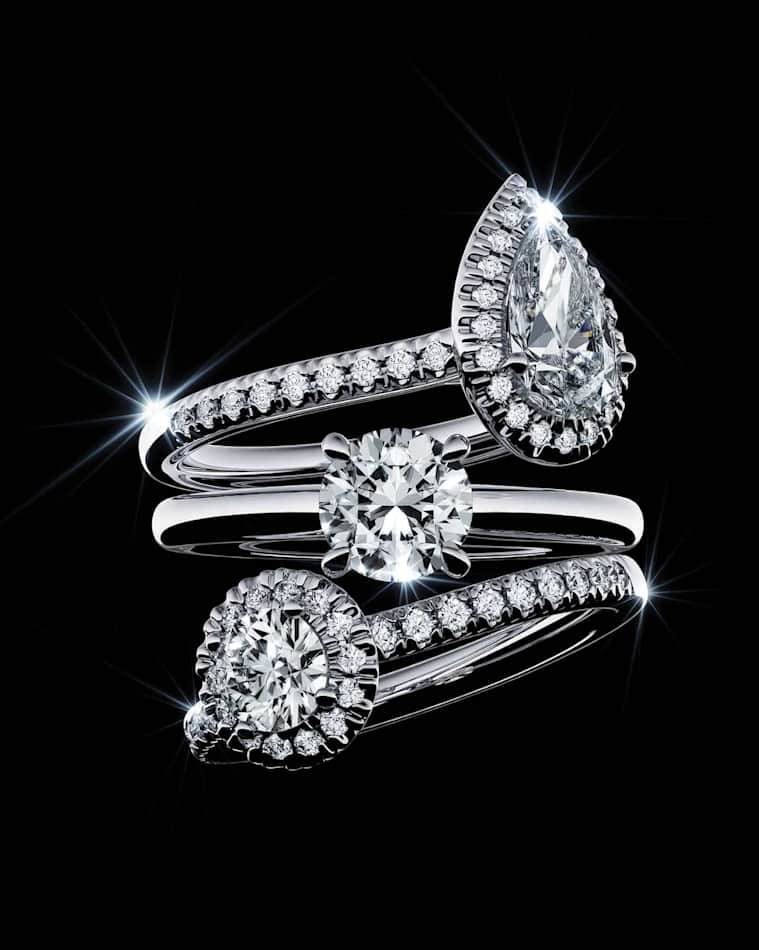
ダイヤモンドの4Cとは?
Title:ダイヤモンドの品質を評価する基準として全世界で使われている4Cは、ストーンの品質と価値を決定します。4Cとは、カラー、カット、カラット、そしてクラリティを指します。Swarovski Created Diamondsコレクションのラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドは、International Gemological Institute(IGI)の鑑定を受け、ダイヤモンドの4Cに準じてその品質が認証されており、カラーはG以上、クラリティはVS以上など、優れた品質が認められたラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドのみが使われることを許されます。
クラリティの原則と要素
Title:ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドのクラリティはインクルージョンやブレミッシュの有無や位置によって評価されますが、ダイヤモンドに独特の個性と魅力を与えてくれる要因でもあります。クラリティの詳細をご覧ください。
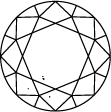
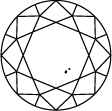
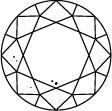



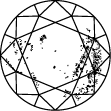

ダイヤモンドのクラリティを表すチャート
Title:ダイヤモンドのクラリティ・スケールとグレード
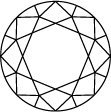
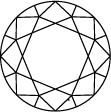
Subtitle:ダイヤモンドのクラリティ・スケールはIFからI3までに分かれており、ストーンの中に含まれるインクルージョンやブレミッシュの数や位置に基づいています。ダイヤモンドのクラリティのグレードは、標準条件における10倍拡大下で見えるインクルージョンで決定されます。IFは内部にインクルージョンが無いダイヤモンドを表しますが、クラリティ・スケールで反対の位置にあるI3は、インクルージョンやブレミッシュがはっきり見えることを示しています。真に欠陥のないダイヤモンドは非常に稀であり、ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドをはじめとするほとんどのストーンには、何らかのインクルージョンやブレミッシュが含まれています。
カットの原則と要素
Title:ラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドのカットのグレードは、プロポーション、シンメトリー、ポリッシュの3つの要素に基づいて評価されます。高い技術者によるカットだからこそ、光を吸収して反射するファセットが数多く生まれ、ストーンがあらゆる角度からきらめきます。

ダイヤモンドのカラースケールとチャート
ダイヤモンドのカラーはDからZまでのスケールで評価され、Dは黄色味のない透明なアイスホワイトですが、Zは黄色や茶色の色合いです。チャートのアルファベットが示す範囲はストーンの色合いを示しており、DからFまでは無色、SからZまでは薄い黄色または茶色の色合いであることを意味しています。Swarovski Created Diamondsコレクションには、無色からほとんど無色(D~G)である最高級のラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドのみが使用されています。
カラーの原則と要素
Title:









ダイヤモンドのカラット
Title:ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドのカラット・スケール
Subtitle:カラットの語源は、古代の商人がダイヤモンドの重さを測る時の基準として使用していた「イナゴマメ(carob)」の種子に由来します。カラットは、ダイヤモンドの重さを測る国際標準計量単位です。1カラットは0.2gで、5カラットのダイヤモンドの重量は1gになります。ダイヤモンドのカラットはストーンの大きさではなく、単にその重さを指します。ダイヤモンドは通常、カラット数が大きくなるにつれ高価になります。
Swarovski Created Diamondsのすべて
Title:ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンド
Subtitle:伝統と最新のトレンドを融合した卓越した芸術性が表現され、ダイヤモンドの未来を再定義したSwarovski Created Diamondsコレクションの世界をご覧ください。まるで別世界のような輝きを放つ星々のコレクションから、純粋なエレガンスが感じられるシグネチャーアイテムまで、永遠に愛用したいスタイルが見つかります。
ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドを手に入れる
Title:理想のアイテムを見つけましょう
Subtitle:ブランドDNAの自然な進化として生まれたSwarovski Created Diamondsは巧みなカットと力強い輝きが特徴のラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドで、採掘されたダイヤモンドとの唯一の違いはどこで生成されるかであり、それ以外のすべては100%同じです。ダイヤモンドの種結晶から少しずつ層を重ねて大きくなり、成長したラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドは、完璧にカットし研磨されて至高の輝きを放ちます。
ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドとは?
Title:ラボグロウン・ダイヤモンドを知る
Subtitle:地中でダイヤモンドが生成されるプロセスを再現した環境下でラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドがどのように出来上がるかを詳しく見てみましょう。Swarovski Created Diamondsコレクションのさまざまなカットのダイヤモンドと、デザインを生み出すきっかけとなったインスピレーションをご覧ください。
ダイヤモンドを詳しく知る
高貴な輝き
よくある質問
ダイヤモンドの4Cに関するQ&A
4Cとは何ですか?
すべてのダイヤモンドは他のどのダイヤモンドとも微妙に異なり、唯一無二の特徴を持っています。c4Cとは、カラー、クラリティ、カット、カラットを指します。
ダイヤモンドのクラリティは重要ですか?
最高のダイヤモンドのクラリティとは?
ダイヤモンドのクラリティは透明度の事をいい、インクルージョン(内包物)とブレミッシュ(表面の疵)がどれだけ少ないかで評価されます。クラリティを評価するには、ダイヤモンドを10倍拡大下で鑑定します。表面のブレミッシュと内部のインクルージョンの数やタイプ、サイズ、位置などによってグレードが決まります。
宝石鑑定士は、ダイヤモンドを最高品質のIF(インターナリーフローレス)からI3(インクルーデッド)で評価します。
ラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドは内外部にまったく傷がないのですか?
いいえ。採掘されたダイヤモンドでもラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドでも、ほぼすべてのダイヤモンドにはインクルージョンが含まれています。ラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドの場合、金属のインクルージョンがある場合があります。宝石鑑定士がダイヤモンドの中に金属の痕跡を見つけた場合、それはラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドであると考えることができます。インクルージョンのあるラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドは存在しますが、SwarovskiではInternational Gemological Institute(IGI)が4Cに従って鑑定し、認証した優れた品質のダイヤモンドのみをSwarovski Created Diamondsコレクションで使用しています。
ラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドは曇りますか?
いいえ。ラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドは時間が経っても曇りません。ラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドは採掘されたダイヤモンドと、物理的および化学的に100%同じ特性を持っており、時間の経過とともに劣化したり外観が変化したりすることはありません。グレードの低いダイヤモンドの種結晶が使用されたラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドの中には、不純物による色合いや結晶構造の欠陥といったものが含まれる場合がありますが、Swarovski Created Diamondsコレクションに使用されているされるラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドは非常に高い品質を誇り、優れた輝きを放ちます。
ラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドはどのように認定され、格付けされますか?
Swarovski Created Diamondsコレクションに使用されているラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドは、International Gemological Institute(IGI)の鑑定を受け、ダイヤモンドの4Cに準じてその品質が認証されており、IGIによるデジタルのラボレポートが付属しています。
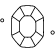
ダイヤモンドのファセットとは?
ファセットとは、ダイヤモンドの表面を構成する平らな面を表す用語で、ファセットに表面反射、内部反射することで光を分散させます。
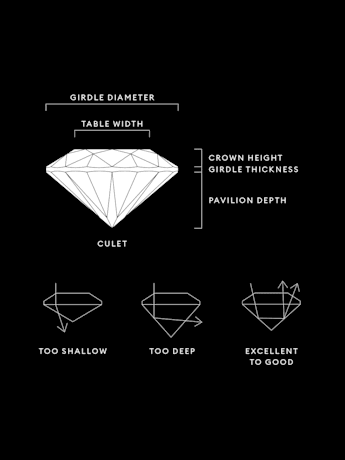
ダイヤモンドのカット品質はどのように決まるのですか?
ダイヤモンドのカットは形状(ラウンド、ハート、楕円形、マーキス、ペア)のことだと思われがちですが、ダイヤモンドカットのグレードは、ダイヤモンドのファセットが光とどのように相互作用するのかを評価します。ダイヤモンドのカットのグレードは、プロポーション、シンメトリー、ポリッシュの3つの要素に基づいて評価されます。ラウンドブリリアントカットのダイヤモンドは、ExcellentからPoorまでのスケールで正式なカットグレードが決められます。 すべてのラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドが最高の状態で光を吸収して反射し、その美しさと輝きが最大限に活かされるよう、Swarovskiはカットの品質に妥協を許しません。
最高のダイヤモンドカットとは?
ダイヤモンドカットのグレードは、カットとは、ダイヤモンドのファセットが光とどのように相互作用してファイアーを導き出すかを表すものです。それぞれのストーンに個性を与えるのはカットであり、プロポーション、対称性、および精密なカットの角度を完璧にすることで、ラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドに素晴らしい輝きが生まれます。ダイヤモンドの評価は、ダイヤモンドカットのチャートのプロポーション、シンメトリー、ポリッシュという3つの要素によって決まりますが、輝きには最高のストーンカットが一番重要です。 浅すぎず深すぎず、幅と深さのバランスがシンメトリーになるカットが最高とされています。ダイヤモンドの内部を通過する光の完璧な屈折点を作り出し、光をダイヤモンド内で反射させ、磨かれた輝きを際立たせます。
ダイヤモンドのカラーはどのように決まるのでしょうか?
カラーとは、ホワイトダイヤモンドに固有の自然な色合いを指します。カラーグレーディングの業界基準では、マスターストーンに照らしてダイヤモンドを評価し、D(カラーレス)からZ(ライトカラー)までのアルファベットでグレードを評価します。 ダイヤモンドは無色に近いほど品質が高いとされています。
ラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドに傷はありますか?
グレードの低いダイヤモンドの種結晶が使用されたラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドの中には、不純物による色合いや結晶構造の欠陥といったものが含まれる場合がありますが、優れた品質が認められたラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドのみがSwarovski Created Diamondsコレクションに使用されることを許されます。
ダイヤモンドのカラット重量とは?
カラットはラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドをはじめとする宝石の重さを測る際に使われる重さの単位です。カラット数が大きくてもそれほど大きく見えない場合や、同じカラット数でもカットの深さによって見た目の大きさが違う場合があります。1カラットは0.2gで、100分の1カラットまで表示されます。
ダイヤモンドのカラット重量とは何ですか?どのように測定され、またどのくらい重要ですか?
カラットはラボラトリー・グロウン・ダイヤモンドをはじめとする宝石の重さを測る際に使われる重さの単位です。ダイヤモンドのカラットはストーンの大きさではなく、単にその重さを指します。1カラットは100分の1まで表示されるため、 小数点以下2桁までの正確な測定が可能になります。1カラット未満のダイヤモンドの重量は、その小数点以下の数字だけで示されている場合もあります。ダイヤモンドは通常、カラット数が大きくなるにつれ高価になりますが、お好みやライフスタイルによってベストなダイヤモンドを選びましょう。
ダイヤモンドはカラットが高いほうが良いのでしょうか?
お客様の好みによって選んでいただくことが重要です。より大きなダイヤモンドをお探しの場合は、カラット数が大きくなるにつれ高価になります。