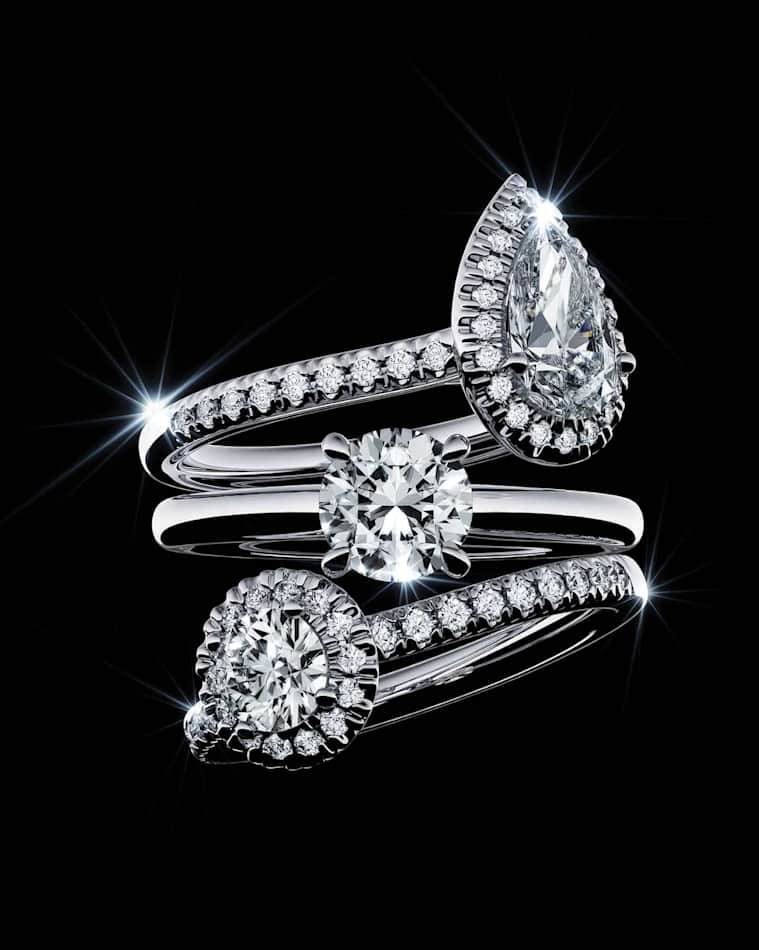
What are the 4Cs of Diamonds?
Title:Clarity Principles and Factors
Title:The clarity of a lab grown diamond is judged by its flaws, which means the inclusions and blemishes that give it unique character and charm. Discover more about diamond clarity below.
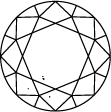
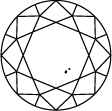
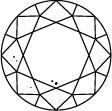



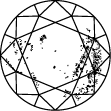

Diamond Clarity Chart
Title:Diamond clarity scale and grades
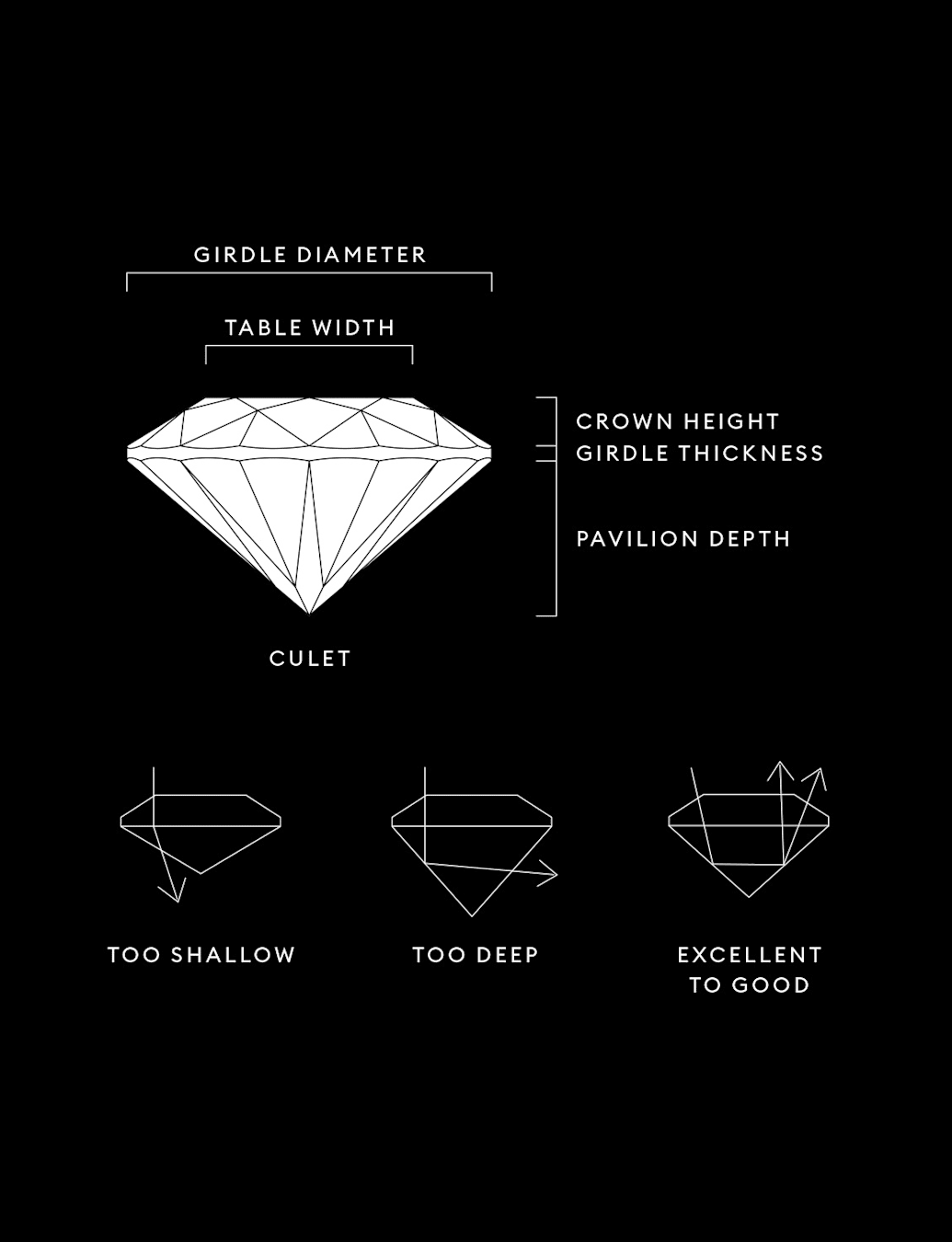
Subtitle:Cut Principles and Factors
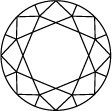
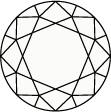
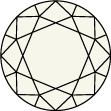
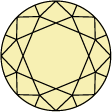
Title:The quality of how a lab grown diamond is cut is based on its proportions, symmetry, and polish. An expert cut creates a multitude of facets, absorbing and reflecting the light so the stone shimmers from every angle.

Title:
Subtitle:
Diamond color scale and chart
Diamond coloring is rated on a scale from D to Z, with D clear ice white with no hint of yellow, while those rated Z are shades of yellow and brown. Each letter range on the chart denotes a shade of stone, with those rated D to F appearing colorless, through to S to Z appearing in shades of light yellow or brown. Swarovski only accepts the finest lab grown diamonds in its collections, meaning they range from colorless to nearly colorless diamonds (D-G).
Color Principles and Factors
Title:









Diamond Carat Weight
Title:Lab Grown Diamond Carat Scale
Subtitle:All About Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds
Subtitle:Discover the world of Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry, redefining the future of diamonds with exceptional collections that bridge the gap between tradition and current trends. From the otherworldly brilliance of our interstellar collection to the pure elegance of our signature pieces, find a style that will last a lifetime.
Lab Grown Diamonds Buying Guide
Title:Find the perfect piece
Subtitle:What are Laboratory Grown Diamonds?
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds explained
Subtitle:Frequently asked questions
Diamond 4Cs FAQs
What are the 4Cs?
Is diamond clarity important?
What is the highest diamond clarity?
In order to assess clarity, the diamond is inspected under 10x power magnification. The number and nature of external (blemishes), and internal characteristics (inclusions), as well as their size and position, determine the grade.
Gemologists grade diamonds from Internally Flawless (IF) as the highest quality to Included (I3).
Are laboratory grown diamonds flawless?
Do laboratory grown diamonds get cloudy?
How are laboratory grown diamonds certified and graded?
What are diamond facets?
How is diamond cut quality determined?
What is the best diamond cut?
How is a diamond’s color determined?
The closer the diamond is to being colorless, the higher its quality.