Que signifie 4C ?
Title:Clarté : principes et facteurs
Title:On jugera la clarté d’un diamant créé en laboratoire en fonction de ses défauts. Ce sont ses inclusions et ses imperfections qui lui prêtent un charme et un caractère uniques. Retrouvez ci-dessous plus d’informations sur la clarté du diamant.
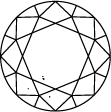
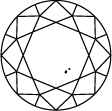
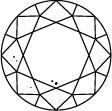



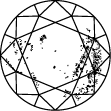

Gráfica de pureza del diamante
Title:Grados y escala de pureza del diamante
Subtitle:La escala de pureza del diamante va de IF a I 3 y se basa en el número de inclusiones e imperfecciones que contiene cada piedra. El grado de pureza de un diamante se establece bajo condiciones de visualización estándar con un aumento de 10x. El IF representa un diamante interiormente perfecto, mientras que en el otro extremo de la gráfica de pureza de un diamante, el I 3 indica la inclusión de una imperfección visible. Los diamantes totalmente perfectos son muy escasos. Prácticamente todas las piedras, incluidos los diamantes creados en laboratorio, tienen algún tipo de inclusión.
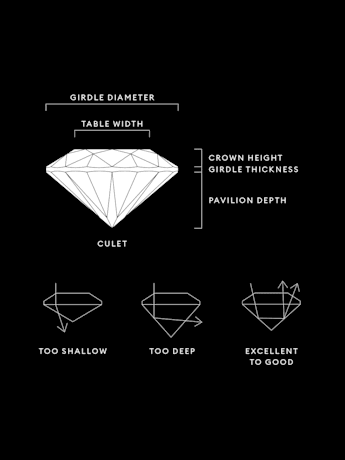
Principios y factores de la talla
Title:La calidad de la talla de un diamante creado en laboratorio se basa en las proporciones, la simetría y el pulido. Una talla experta crea muchas facetas que absorben y reflejan la luz, lo que permite que una piedra brille desde cada ángulo.

Escala y gráfica de color del diamante
El color del diamante se califica según una escala de la D a la Z, en la que la D corresponde al blanco hielo transparente sin ningún tono de amarillo, y la Z a los que tienen tonos amarillos y marrones. Cada intervalo de letras de la gráfica representa una coloración de la piedra: de la D a la F para las piedras incoloras y de la S a la Z para las que tienen tonos amarillos claros o marrones.Swarovski solo incluye en las colecciones diamantes creados en laboratorio de la más alta calidad, con piedras de incoloras a casi incoloras (D-G)
Principios y factores del color
Title:Las piedras incoloras son las más buscadas en el mundo de los diamantes, ya que son muy escasas. Los Swarovski Created Diamonds se evalúan según una escala estandarizada del color del diamante.










Diamond Carat Weight
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamond Carat Scale
Subtitle:All About Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds
Subtitle:Laboratory Grown Diamonds Buying Guide
Title:Find the perfect piece
Subtitle:What are Laboratory Grown Diamonds?
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds explained
Subtitle:Frequently asked questions
Diamond 4Cs FAQs
What are the 4Cs?
Is de helderheid van een diamant belangrijk?
Wat is de hoogste helderheidsgraad van een diamant?
Om de zuiverheid te beoordelen, wordt de diamant bekeken met een vergrotingsfactor van 10x. Het aantal en de aard van de externe (onzuiverheden) en interne kenmerken (insluitsels), evenals hun grootte en positie, bepalen de graad.
Gemologen beoordelen diamanten van Internally Flawless (IF) als de hoogste kwaliteit tot Included (I3).
Zijn laboratorium-diamanten foutloos?
Worden laboratorium-diamanten troebel?
Hoe worden laboratorium-diamanten gecertificeerd en beoordeeld?
Wat zijn diamantfacetten?
Hoe wordt de kwaliteit van de slijpvorm bepaald?
Wat is de beste slijpvorm voor diamanten?
Hoe wordt de kleur van een diamant bepaald?
Hoe kleurlozer de diamant is, hoe hoger de kwaliteit.