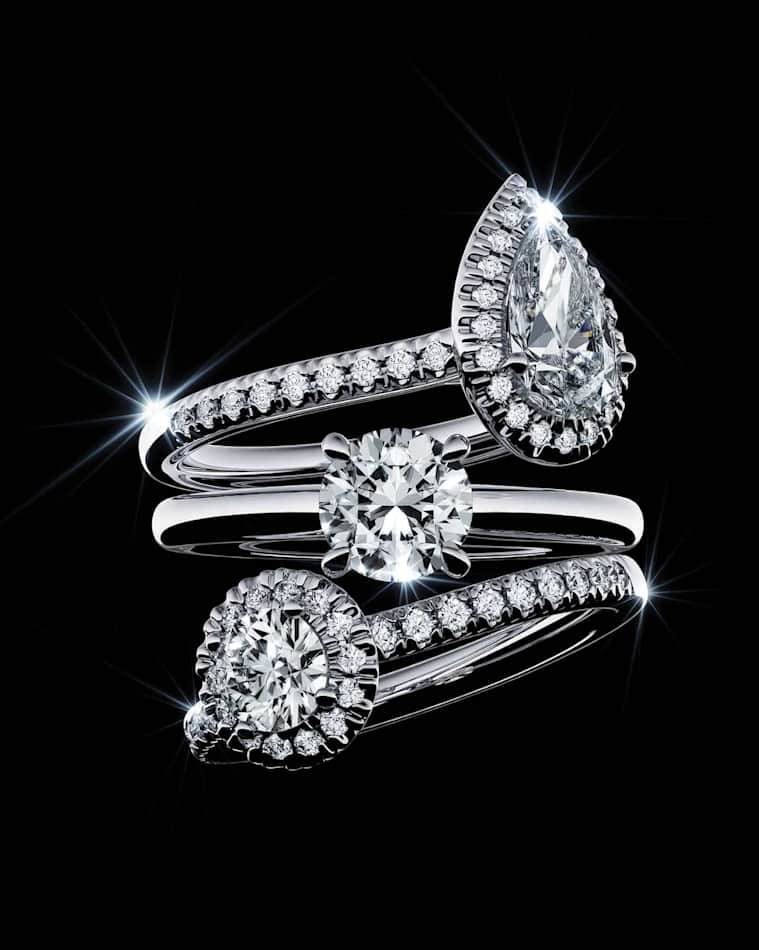
¿Qué son las 4 C del diamante?
Title:Principios y factores de la pureza
Title:La pureza de un diamante creado en laboratorio se establece por sus defectos, que son las inclusiones e imperfecciones que le dan su carácter y encanto único. Más abajo, descubre más sobre la pureza del diamante.
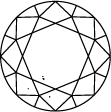
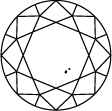
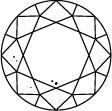



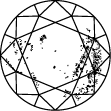

Gráfica de pureza del diamante
Title:Grados y escala de pureza del diamante
Subtitle:La escala de pureza del diamante va de IF a I 3 y se basa en el número de inclusiones e imperfecciones que contiene cada piedra. El grado de pureza de un diamante se establece bajo condiciones de visualización estándar con un aumento de 10x. El IF representa un diamante interiormente perfecto, mientras que en el otro extremo de la gráfica de pureza de un diamante, el I 3 indica la inclusión de una imperfección visible. Los diamantes totalmente perfectos son muy escasos. Prácticamente todas las piedras, incluidos los diamantes creados en laboratorio, tienen algún tipo de inclusión.
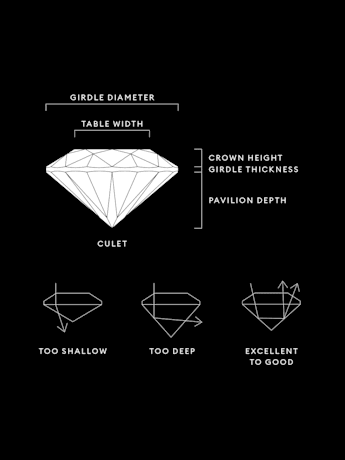
Principios y factores de la talla
Title:La calidad de la talla de un diamante creado en laboratorio se basa en las proporciones, la simetría y el pulido. Una talla experta crea muchas facetas que absorben y reflejan la luz, lo que permite que una piedra brille desde cada ángulo.
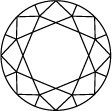
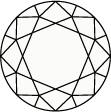
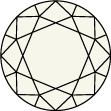

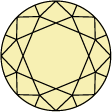
Escala y gráfica de color del diamante
El color del diamante se califica según una escala de la D a la Z, en la que la D corresponde al blanco hielo transparente sin ningún tono de amarillo, y la Z a los que tienen tonos amarillos y marrones. Cada intervalo de letras de la gráfica representa una coloración de la piedra: de la D a la F para las piedras incoloras y de la S a la Z para las que tienen tonos amarillos claros o marrones.Swarovski solo incluye en las colecciones diamantes creados en laboratorio de la más alta calidad, con piedras de incoloras a casi incoloras (D-G)
Principios y factores del color
Title:Las piedras incoloras son las más buscadas en el mundo de los diamantes, ya que son muy escasas. Los Swarovski Created Diamonds se evalúan según una escala estandarizada del color del diamante.










Peso en quilates del diamante
Title:Escala de quilates de los diamantes creados en laboratorio
Subtitle:La medición en quilates proviene de la palabra «carob», una semilla que los comerciantes de la antigüedad utilizaban como referencia para pesar los diamantes. El quilate es una unidad de medida estándar internacional para pesar el diamante. Un quilate equivale a 200 miligramos, de manera que 5 quilates equivalen a 1 gramo. Los quilates del diamante no hacen referencia al tamaño de la piedra, sino únicamente a su peso. Los diamantes con más quilates suelen ser más caros.
Todo sobre Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Diamantes creados en laboratorio
Subtitle:Descubre el mundo de la joyería Swarovski Created Diamonds, joyas que redefinen el futuro de los diamantes, con colecciones excepcionales que unen tradición y últimas tendencias. Encuentra el estilo para ti, para toda la vida, desde el increíble brillo de nuestra colección interestelar hasta la más pura elegancia de nuestras piezas de firma.
Guía de compra de los diamantes creados en laboratorio
Title:Encuentra la pieza perfecta para ti
Subtitle:Siguiendo la evolución natural del ADN de nuestra marca, la joyería Swarovski Created Diamonds ofrece diamantes creados en laboratorio con una talla maestra, intensamente brillantes e idénticos en todo a sus homólogos, excepto en el origen. Se forman capa a capa a partir de una semilla de carbono, reflejando perfectamente todo su brillo natural.
¿Qué son los diamantes creados en laboratorio?
Title:Explicamos los diamantes creados en laboratorio
Subtitle:Preguntas frecuentes
Preguntas frecuentes de las 4 C del diamante
¿Qué son las 4 C?
¿La pureza del diamante es importante?
¿Cuál es la pureza máxima del diamante?
Para valorar la pureza, el diamante se observa bajo un aumento de 10x. El número y la naturaleza de las características externas (imperfecciones) e internas (inclusiones), así como el tamaño y la posición, determinan su calificación.
Los gemólogos califican el diamante desde Internamente perfecto (IF), que es el de máxima calidad, hasta Con inclusiones (I3).
¿Los diamantes creados en laboratorio son perfectos?
¿Los diamantes creados en laboratorio se vuelven opacos con el tiempo?
¿Cómo se califican y se certifican los diamantes creados en laboratorio?
¿Qué son las facetas de un diamante?
¿Cómo se determina la calidad de la talla de un diamante?
¿Cuál es la mejor talla de diamante?
¿Cómo se determina el color de un diamante?
Cuanto más incoloro sea el diamante, más calidad tendrá.