What Are the 4Cs of Diamonds?
Title:Clarity Principles and Factors
Title:
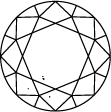
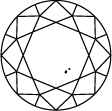
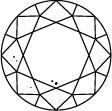



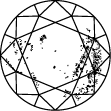

Diamond Clarity Chart
Title:Diamond clarity scale and grades
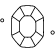
Subtitle:Cut Principles and Factors
Title:

Diamond color scale and chart
Diamond coloring is rated on a scale from D to Z, with D clear ice white with no hint of yellow, while those rated Z are shades of yellow and brown. Each letter range on the chart denotes a shade of stone, with those rated D to F appearing colorless, through to S to Z appearing in shades of light yellow or brown. Swarovski only accepts the finest laboratory grown diamonds in its collections, meaning they range from colorless to nearly colorless diamonds (D-G).
Color Principles and Factors
Title:









Diamond Carat Weight
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamond Carat Scale
Subtitle:All About Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds
Subtitle:Laboratory Grown Diamonds Buying Guide
Title:Find the perfect piece
Subtitle:What are Laboratory Grown Diamonds?
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds explained
Subtitle:Frequently asked questions
Diamond 4Cs FAQs
What are the 4Cs?
Is diamond clarity important?
What is the highest diamond clarity?
In order to assess clarity, the diamond is inspected under 10x power magnification. The number and nature of external (blemishes), and internal characteristics (inclusions), as well as their size and position, determine the grade.
Gemologists grade diamonds from Internally Flawless (IF) as the highest quality to Included (I3).
Are laboratory grown diamonds flawless?
Do laboratory grown diamonds get cloudy?
How are laboratory grown diamonds certified and graded?
What are diamond facets?
How is diamond cut quality determined?
What is the best diamond cut?
How is a diamond’s color determined?
The closer the diamond is to being colorless, the higher its quality.
Do laboratory created diamonds have blemishes?
What is diamond carat weight?
What is the carat weight of a diamond, how is it measured and how important is it?
Il peso in carati è l’unità di peso standard dei diamanti e la prima caratteristica che viene presa in considerazione per il processo di valutazione. Il peso in carati del diamante è la determinazione del peso del diamante. Ogni carato può essere suddiviso in 100 “punti”. Ciò consente misurazioni precise al centesimo decimale. Il peso di un diamante inferiore a un carato può essere definito esclusivamente dai suoi “punti”. Più grande è il diamante, maggiori saranno i carati, ma solo tu puoi decidere che importanza dare alla grandezza.
È meglio avere un diamante di caratura superiore?
Questa è una questione del tutto personale. Se desideri un diamante più grande, opta per una caratura superiore poiché questa indica il peso e quindi la dimensione del diamante.