What Are the 4Cs of Diamonds?
Title:Clarity Principles and Factors
Title:
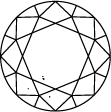
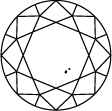
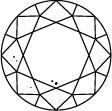



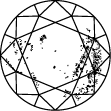

Diagramma di purezza del diamante
Title:Scala e gradi di purezza del diamante
Subtitle:La scala di purezza del diamante va da I.F a I3 e si basa sul numero di inclusioni e imperfezioni riscontrate in ogni pietra. I gradi di purezza del diamante sono determinati in condizioni di visualizzazione standard con lente di ingrandimento 10x. La categoria I.F indica un diamante privo di inclusioni interne mentre, all’altra estremità del diagramma di purezza del diamante, I3 indica l’inclusione di un’imperfezione visibile. I diamanti completamente privi di inclusioni sono estremamente rari. Quasi tutte le pietre, compresi i diamanti creati in laboratorio, presentano inclusioni di qualche tipo.
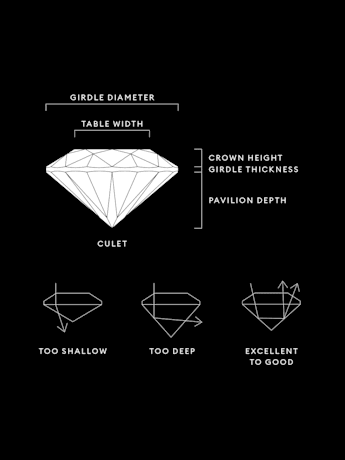
Parametri e fattori di taglio
Title:La qualità del taglio di un diamante creato in laboratorio è determinata dalle sue proporzioni, dalla sua simmetria e dalla sua lucidatura. Un taglio a regola d'arte crea molteplici sfaccettature che assorbono e riflettono la luce e fanno brillare la da ogni angolazione.

Scala e diagramma di colore del diamante
La colorazione dei diamanti è valutata su una scala da D a Z, in cui D indica un colore bianco ghiaccio limpido senza alcun accenno di giallo, mentre i diamanti classificati con Z presentano sfumature di giallo e marrone. Ogni lettera sul diagramma definisce una sfumatura della pietra: quelle classificate da D a F appaiono incolori, mentre quelle classificate da S a Z presentano tonalità giallo chiaro o marrone. Swarovski include nelle sue collezioni esclusivamente i diamanti creati in laboratorio della massima qualità, ovvero diamanti classificati da incolori a quasi incolori (fascia D-G).
Parametri e fattori cromatici
Title:Le pietre incolori sono le più richieste nel mondo dei diamanti e sono estremamente rare. Gli Swarovski Created Diamonds vengono valutati secondo la scala standardizzata per il colore dei diamanti.










Peso in carati del diamante
Title:Scala di caratura dei diamanti creati in laboratorio
Subtitle:Il nome della misurazione in carati deriva dalla parola “carruba”, un seme che veniva utilizzato come riferimento per il peso dei diamanti dai commercianti del mondo antico. I carati sono un’unità di misura standard internazionale per il peso di un diamante. Un carato equivale a 200 milligrammi, un diamante da 5 carati pesa dunque un grammo. Il carato del diamante non si riferisce alla dimensione di una pietra ma al suo peso. I diamanti diventano in genere più costosi con l’aumentare della loro caratura.
Tutto su Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Diamanti creati in laboratorio
Subtitle:Scopri l’universo dei gioielli Swarovski Created Diamonds che ridefiniscono il futuro dei diamanti con eccezionali collezioni e colmano il divario tra tradizione e tendenze attuali. Dalla brillantezza ultraterrena della nostra collezione interstellare alla pura eleganza delle nostre iconiche creazioni, trova il gioiello da custodire per sempre.
Guida all’acquisto di diamanti creati in laboratorio
Title:Trova il gioiello perfetto
Subtitle:Evoluzione naturale del DNA del nostro marchio, i gioielli Swarovski Created Diamonds sono impreziositi da diamanti creati in laboratorio, magistralmente tagliati, di intensa brillantezza, e identici in tutto e per tutto ai loro omologhi estratti in miniera, tranne che per la loro origine. Formati strato dopo strato da un seme di carbonio, riflettono fedelmente la radiosità della natura.
Che cosa sono i diamanti creati in laboratorio?
Title:I diamanti creati in laboratorio spiegati al pubblico
Subtitle:Scopri di più sui diamanti creati in laboratorio e su come viene replicato il processo di generazione dei diamanti nel sottosuolo. Scopri i diversi tagli di diamanti delle collezioni Swarovski Created Diamonds, nonché l’ispirazione che si cela dietro ciascun modello.
Domande frequenti
FAQ sulle 4C del diamante
Che cosa sono le 4C?
Ogni diamante differisce lievemente dall’altro e presenta caratteristiche distintive. I nostri diamanti creati in laboratorio sono diamanti al 100% e, proprio come i diamanti estratti in miniera, vengono classificati secondo le 4C per la valutazione di qualità del diamante. Le 4C sono le abbreviazioni di color (colore), clarity (purezza), cut (taglio) e carat weight (peso in carati) e rappresentano gli standard universalmente riconosciuti per valutare la qualità di un diamante.
La purezza del diamante è importante?
A un maggiore grado di purezza corrispondono minori inclusioni o imperfezioni del diamante. Questo conferisce al diamante una qualità superiore rispetto ad un altro diamante di grado inferiore.
Qual è la massima purezza del diamante?
La purezza del diamante è una valutazione della perfezione della pietra classificata in base alla visibilità di due tipi di caratteristiche: inclusioni e imperfezioni.
Per valutarne la purezza, il diamante viene esaminato con una lente di ingrandimento 10x. Il numero e la natura di caratteristiche esterne (imperfezioni) e interne (inclusioni), nonché la loro dimensione e posizione, determinano il grado di purezza.
I gemmologi classificano i diamanti dal grado di qualità più alta, Internally Flawless (IF, privo di inclusioni), al grado Included (I3, incluso).
I diamanti creati in laboratorio sono di qualità ineccepibile?
No, quasi tutti i diamanti (estratti o creati in laboratorio) presentano inclusioni. Nei diamanti di laboratorio possono verificarsi inclusioni metalliche. Se un esperto individua una traccia di metallo in un diamante, può presumere che sia stato creato in laboratorio. Sebbene esistano diamanti artificiali che presentano difetti, Swarovski utilizza esclusivamente quelli di alta qualità e certificati dall’Istituto Gemmologico Internazionale (IGI) secondo le 4C, in modo da garantire che solo diamanti della migliore qualità siano inclusi nelle collezioni Swarovski Created Diamonds.
I diamanti creati in laboratorio diventano opachi?
No, i diamanti creati in laboratorio non si opacizzano col tempo. Sono identici al 100% ai diamanti con le stesse proprietà fisiche e chimiche e non si degradano e non cambiano aspetto nel tempo. Se sono stati utilizzati semi di diamante di scarsa qualità, alcuni diamanti di laboratorio presentano difetti evidenti, come sfumature di colore dovute a impurità nel diamante o imperfezioni strutturali del cristallo. I diamanti creati in laboratorio elaborati nei gioielli Swarovski Created Diamonds soddisfano u o standard di qualità molto elevato e non presentano caratteristiche innaturali e problematiche.
Come vengono certificati e classificati i diamanti creati in laboratorio?
I diamanti creati in laboratorio elaborati nei gioielli Swarovski Created Diamonds vengono selezionati manualmente ed esaminati da gemmologi esperti per garantire che soddisfino i nostri elevati standard di qualità. Ogni gioiello delle collezioni Galaxy ed Eternity è accompagnato da un rapporto di laboratorio digitale redatto dall’Istituto Gemmologico Internazionale (IGI).
Che cosa sono le sfaccettature del diamante?
Le sfaccettature del diamante si riferiscono ad ognisuperficie piana che crea la forma di un diamante. Ogni diamante presenta molteplici sfaccettature che gli consentono di assorbire e riflettere la luce.
Come si determina la qualità del taglio del diamante?
Spesso si pensa al taglio di un diamante come alla sua forma (rotonda, a cuore, ovale, marchesa, pera), ma il taglio del diamante si riferisce in realtà alla qualità dell’interazione delle sue sfaccettature con la luce. Il taglio di un diamante è la sintesi della qualità della forma, della geometria e della finitura del diamante. I diamanti rotondi e brillanti vengono classificati formalmente su una scala che varia da Ideal (il migliore) a Poor (di scarsa qualità). Swarovski non scende a compromessi quando si tratta della qualità del taglio e garantisce che tutti i nostri diamanti creati in laboratorio offrano una resa di luce e una brillantezza ottimali.
Qual è il miglior taglio di diamante?
Il taglio si riferisce al modo in cui le sfaccettature del diamante interagiscono con la luce per rivelarne il fulgore interiore. Il taglio conferisce ad ogni diamante una personalità unica, mentre il perfezionamento delle proporzioni, la simmetria e le angolazioni tagliate con precisione degli Swarovski Created Diamonds conferiscono loro una brillante lucentezza. Il taglio migliore presenta un equilibrio tra larghezza e profondità per creare simmetria; inoltre, non è né troppo superficiale né troppo profondo, ma crea il punto perfetto di rifrazione della luce attraverso il diamante, riflettendola all'interno dello stesso e mettendone in evidenza la brillante lucidatura.
Come viene determinato il colore di un diamante?
Il colore si riferisce alla tinta naturale inerente ai diamanti bianchi. Lo standard industriale per la classificazione del colore consiste nel valutare ogni diamante rispetto a un set di riferimento e nell’assegnare un voto in lettere da D (incolore) a Z (giallo chiaro).
Più il diamante si avvicina all'incolore, più la sua qualità è elevata.
I diamanti creati in laboratorio presentano imperfezioni?
Se sono stati utilizzati semi di diamante di scarsa qualità, alcuni diamanti creati in laboratorio presentano difetti evidenti, come sfumature di colore dovute a impurità o imperfezioni strutturali. Swarovski non commercializza diamanti creati in laboratorio che presentano caratteristiche innaturali e problematiche.
Che cos’è il peso in carati del diamante?
Il carato è l’unità utilizzata specificamente per determinare il peso delle pietre preziose, compresi i diamanti creati in laboratorio. Un diamante può avere un peso in carati superiore senza per questo essere di dimensioni maggiori, e due diamanti dello stesso peso in carati possono avere dimensioni diverse se uno viene tagliato più in profondità dell’altro. Un carato pesa un quinto di grammo ed è suddiviso in 100 punti.
Che cos’è il peso in carati di un diamante, come si misura e quanto è importante?
Il peso in carati è l’unità di peso standard dei diamanti e la prima caratteristica che viene presa in considerazione per il processo di valutazione. Il peso in carati del diamante è la determinazione del peso del diamante. Ogni carato può essere suddiviso in 100 “punti”. Ciò consente misurazioni precise al centesimo decimale. Il peso di un diamante inferiore a un carato può essere definito esclusivamente dai suoi “punti”. Più grande è il diamante, maggiori saranno i carati, ma solo tu puoi decidere che importanza dare alla grandezza.
È meglio avere un diamante di caratura superiore?
Questa è una questione del tutto personale. Se desideri un diamante più grande, opta per una caratura superiore poiché questa indica il peso e quindi la dimensione del diamante.