Wat zijn de 4 C’s van diamanten?
Title:
De 4C's zijn universeel erkend en vormen een leidraad in de wereld van diamanten. Ze bepalen mede de kwaliteit en waarde van elke steen: de 4C's staan voor color, cut, carat en clarity. De laboratorium-diamanten uit de Swarovski Created Diamond-collecties worden beoordeeld op basis van deze 4 C's door IGI, het International Gemological Institute. De laboratorium-diamanten in deze collecties zijn van zeer goede kwaliteit: G+ in kleur en VS+ in helderheid.
Helderheidsprincipes en -factoren
Title:
De helderheid van een laboratorium-diamant wordt beoordeeld aan de hand van de gebreken, dat wil zeggen de insluitsels en onzuiverheden die de diamant zijn unieke karakter en charme geven. Ontdek hieronder meer over de helderheid van diamanten.
I.F.
Internally flawless (intern foutloos)
VVS 1
VVS 2
Very very slightly included (heel erg kleine inclusie)
VS 1
VS 2
Very slightly included (zeer geringe inclusie)
SI 1

SI 2

Slightly included (lichte inclusie)
I 1

I 2
I 3

Included (insluitsel)
Helderheidstabel voor diamanten
Title:Helderheidstabel en cijfers voor diamanten
Subtitle:
De helderheidstabel van diamanten loopt van I.F. tot I 3 en is gebaseerd op het aantal insluitsels en oneffenheden die in elke steen gevonden worden. De helderheidsgraad van diamanten wordt bepaald onder standaardomstandigheden met een vergroting van 10x. I.F. wordt gebruikt voor een intern foutloze diamant. Aan het andere uiteinde van de helderheidsschaal staat I 3 voor een zichtbare onzuiverheid. Echt foutloze diamanten zijn uiterst zeldzaam; bijna alle stenen, inclusief laboratorium-diamanten, hebben insluitsels van welke aard dan ook.
Kleurprincipes en -factoren
Title:
De kwaliteit van een laboratorium-diamant is gebaseerd op zijn grootte, symmetrie en glans. Een vakkundige slijpvorm creëert een veelheid aan facetten, die het licht absorberen en weerspiegelen zodat de steen vanuit elke hoek schittert.
Kleurloos
D-F
Vrijwel kleurloos
G-J
Enigszins getint
K-M
Zeer lichte kleur

N-R
Lichte kleur
S-Z
Kleurtabel en -kaart voor diamanten
De kleur van diamanten wordt beoordeeld op een schaal van D tot Z, waarbij D helder ijswit is zonder een vleugje geel, en Z geel- en bruintinten bevat. Elk letterbereik op de kaart geeft de tint van de steen aan, waarbij de diamanten met de classificatie D tot en met F kleurloos zijn en de diamanten met de classificatie S tot en met Z een lichtgele of bruine kleur hebben. Swarovski accepteert alleen de beste laboratorium-diamanten in zijn collecties, waardoor ze variëren van kleurloos tot bijna kleurloos (D-G).
Kleurprincipes en -factoren
Title:
Kleurloze stenen zijn de meest populaire diamanten en uiterst zeldzaam. Swarovski Created Diamonds worden beoordeeld aan de hand van de gestandaardiseerde kleurenschaal voor diamanten.

2,5 mm
0,05 CT

3 mm
0,10 CT

3,8 mm
0,20 CT

4,5 mm
0,30 CT

4,8 mm
0,40 CT

5,2 mm
0,50 CT

5,8 mm
0,70 CT

6,3 mm
0,90 CT

6,5 mm
1,00 CT

6,9 mm
1,25 CT
7,4 mm
1,50 CT
7,8 mm
1,75 CT
8,2 mm
2,00 CT
8,8 mm
2,50 CT
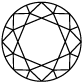
9,4 mm
3,00 CT
Gewicht diamant
Title:Karaattabel laboratorium-diamanten
Subtitle:
De karaat meeteenheid is afgeleid van het woord 'carbo', een zaadje dat in de oudheid door handelaren werd gebruikt als referentie voor het gewicht van diamanten. Karaat is een internationale standaard meeteenheid voor het gewicht van een diamant. Eén karaat is gelijk aan 200 milligram, dus een diamant van 5 karaat weegt één gram. Het karaat van een diamant verwijst niet naar de afmeting van de steen, maar gewoon naar het gewicht. Diamanten worden meestal duurder naarmate hun karaat toeneemt.
Ontdek Swarovski Created Diamonds
Alles over Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Laboratorium-diamanten
Subtitle:
Ontdek de wereld van Swarovski Created Diamonds-sieraden, die de toekomst van diamanten een nieuwe betekenis geven met bijzondere collecties die traditie en trends met elkaar verbinden. Vind een stijl voor altijd, van de buitenaardse schittering van onze interstellaire collectie tot de pure elegantie van onze iconische stukken.
Koopgids laboratorium-diamanten
Title:Vind uw perfecte sieraad
Subtitle:
Swarovski Created Diamonds-sieraden hebben laboratorium-diamanten en zijn een natuurlijke ontwikkeling van ons merk-DNA. Meesterlijk geslepen, intens helder en in elk opzicht identiek aan hun natuurlijke soortgenoten uit de mijnen, behalve wat hun oorsprong betreft. Ze worden laag voor laag gevormd uit een koolstofzaadje en zijn een perfecte reflectie van de schittering van de natuur.
Wat zijn laboratorium-diamanten?
Title:Uitleg laboratorium-diamanten
Subtitle:
Ontdek meer over diamanten die in een laboratorium worden gekweekt en hoe het proces van het nabootsen van de vorming van natuurlijke diamanten tot stand komt. Ontdek de diverse slijpvormen van diamanten in de Swarovski Created Diamond-collecties en de inspiratie achter de ontwerpen.
Veelgestelde vragen
Veelgestelde vragen 4C’s van diamanten
Wat zijn de 4C’s?
Elke diamant verschilt een beetje van de volgende en heeft zijn eigen unieke kenmerken. Laboratorium-diamanten zijn 100% diamanten, en net als natuurlijke diamanten worden onze laboratorium-diamanten beoordeeld volgens de 4C's van diamantbeoordeling. De 4C's zijn color, clarity, cut en carat, en zijn de wereldwijd geaccepteerde normen die worden gebruikt om de kwaliteit van diamanten te beoordelen.
Is de helderheid van een diamant belangrijk?
Hoe hoger de helderheid, hoe minder insluitsels of onzuiverheden een diamant heeft, waardoor de diamant een hogere waarde heeft dan een diamant met een lagere helderheid.
Wat is de hoogste helderheidsgraad van een diamant?
De helderheid van diamanten is een maatstaf voor de zuiverheid van de steen, die wordt bepaald aan de hand van de zichtbaarheid van twee kenmerken: insluitsels en onzuiverheden.
Om de zuiverheid te beoordelen, wordt de diamant bekeken met een vergrotingsfactor van 10x. Het aantal en de aard van de externe (onzuiverheden) en interne kenmerken (insluitsels), evenals hun grootte en positie, bepalen de graad.
Gemologen beoordelen diamanten van Internally Flawless (IF) als de hoogste kwaliteit tot Included (I3).
Om de zuiverheid te beoordelen, wordt de diamant bekeken met een vergrotingsfactor van 10x. Het aantal en de aard van de externe (onzuiverheden) en interne kenmerken (insluitsels), evenals hun grootte en positie, bepalen de graad.
Gemologen beoordelen diamanten van Internally Flawless (IF) als de hoogste kwaliteit tot Included (I3).
Zijn laboratorium-diamanten foutloos?
Nee, bijna alle diamanten (uit de mijnen en uit het laboratorium) hebben insluitsels. Metalen insluitsels kunnen voorkomen in laboratorium-diamanten. Als een expert een spoor van metaal in een diamant ziet, kan diegene ervan uitgaan dat de diamant in het laboratorium is gekweekt. Hoewel laboratorium-diamanten met insluitsels bestaan, gebruikt Swarovski alleen laboratorium-diamanten van hoge kwaliteit die gecertificeerd zijn door het International Gemological Institute (IGI) volgens de 4C's, namelijk om ervoor te zorgen dat alleen diamanten van de hoogste kwaliteit verwerkt worden in de Swarovski Created Diamond-collecties.
Worden laboratorium-diamanten troebel?
Nee, laboratorium-diamanten worden niet troebel na verloop van tijd. Ze zijn 100% identiek aan natuurlijke diamanten met dezelfde fysische en chemische eigenschappen en mogen na verloop van tijd niet minder worden of van uiterlijk veranderen. Als er diamantzaden van slechte kwaliteit zijn gebruikt, bevatten sommige laboratorium-diamanten duidelijke gebreken, zoals kleurafwijkingen door onzuiverheden in de diamant of onvolkomenheden in de kristalstructuur. De laboratorium-diamanten die verwerkt worden in Swarovski Created Diamonds-sieraden zijn van zeer hoge kwaliteit en hebben geen onnatuurlijke, problematische kenmerken.
Hoe worden laboratorium-diamanten gecertificeerd en beoordeeld?
De laboratorium-diamanten die worden verwerkt in Swarovski Created Diamonds-sieraden zijn met de hand geselecteerd en onderzocht door ervaren edelsteenkundigen om er zeker van te zijn dat ze voldoen aan onze hoge kwaliteitsnormen. Elk sieraad uit de Galaxy- en Eternity-collecties heeft een digitaal laboratoriumrapport van het International Gemological Institute (IGI).
Wat zijn diamantfacetten?
Diamantfacetten verwijzen naar elk plat oppervlak dat de vorm van een diamant bepaalt. Elke diamant heeft meerdere facetten waarmee hij licht kan absorberen en weerspiegelen.
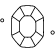
Hoe wordt de kwaliteit van de slijpvorm bepaald?
We denken bij de slijpvorm van een diamant vaak aan de vorm (rond, hart, ovaal, markies, peer), maar de slijpvorm van een diamant betekent eigenlijk hoe goed de facetten van de diamant op het licht reageren. De slijpvorm van een diamant is een maatstaf voor de kwaliteit van de vorm, geometrie en afwerking van de diamant. Ronde briljantgeslepen diamanten krijgen een formeel slijpcijfer op een schaal van Perfect (het beste) tot Slecht. Swarovski sluit geen compromissen op het gebied van slijpkwaliteit om ervoor te zorgen dat al onze laboratorium-diamanten optimale lichtprestaties en schittering hebben.
Wat is de beste slijpvorm voor diamanten?
De slijpvorm verwijst naar de manier waarop de facetten van een diamant reageren op licht om de interne fonkeling te onthullen. Het is de slijpvorm die elke steen zijn persoonlijkheid geeft. Het perfectioneren van de groottes, symmetrie en precisiegeslepen randen van Swarovski Created Diamonds geeft ze hun schitterende glans. De beste slijpvorm heeft een goed evenwicht tussen de breedte en diepte om symmetrie te creëren, niet te ondiep en niet te diep. Dit creëert het perfecte breekpunt van licht, wat in de diamant wordt weerspiegelt en de gepolijste helderheid accentueert.
Hoe wordt de kleur van een diamant bepaald?
Kleur verwijst naar de natuurlijke tint die inherent is aan witte diamanten. De industriestandaard voor het beoordelen van kleur is om elke diamant te beoordelen aan de hand van een originele set en vervolgens een letterclassificatie van D (kleurloos) tot Z (lichtgeel) toe te kennen.
Hoe kleurlozer de diamant is, hoe hoger de kwaliteit.
Hoe kleurlozer de diamant is, hoe hoger de kwaliteit.
Hebben laboratorium-diamanten onzuiverheden?
Wanneer diamantzaden van slechte kwaliteit zijn gebruikt, bevatten sommige laboratorium-diamanten duidelijke gebreken, zoals kleurafwijkingen door onzuiverheden of structurele onvolkomenheden. Swarovski verkoopt geen laboratorium-diamanten met onnatuurlijke, problematische kenmerken.
Wat is het karaatgewicht van een diamant?
Een karaat is een gewichtseenheid die specifiek wordt gebruikt voor edelstenen, inclusief laboratorium-diamanten. Een diamant kan een hoger karaatgewicht hebben zonder groter te lijken, en twee diamanten van hetzelfde karaatgewicht kunnen in grootte verschillen als de ene dieper is geslepen dan de andere. Eén karaat weegt 0,2 gram en is verdeeld in 100 punten.
Wat is het karaatgewicht van een diamant en hoe wordt het gemeten?
Karaatgewicht is de standaard gewichtseenheid voor diamanten en de eerste stap in het beoordelingsproces. Het karaatgewicht van diamanten geeft aan hoeveel een diamant weegt. Elk karaat kan worden onderverdeeld in 100 “punten”. Dit maakt nauwkeurige metingen tot op de honderdste decimaal mogelijk. Het gewicht van een diamant kleiner dan één karaat kan alleen worden omschreven door zijn “punten”. Hoe groter de diamant, hoe meer karaat, maar alleen u kunt beslissen hoe belangrijk dat voor u is.
Is het beter om een diamant met een hoger karaat te kopen?
Dit is een volledig persoonlijke vraag. Als u op zoek bent naar een grotere diamant, kijk dan naar de hoogte van het karaat, omdat dit het gewicht en dus de grootte van de diamant aangeeft.