Wat zijn de 4 C’s van diamanten?
Title:
De 4C's zijn universeel erkend en vormen een leidraad in de wereld van diamanten. Ze bepalen mede de kwaliteit en waarde van elke steen: de 4C's staan voor color, cut, carat en clarity. De laboratorium-diamanten uit de Swarovski Created Diamond-collecties worden beoordeeld op basis van deze 4 C's door IGI, het International Gemological Institute. De laboratorium-diamanten in deze collecties zijn van zeer goede kwaliteit: G+ in kleur en VS+ in helderheid.
Helderheidsprincipes en -factoren
Title:
De helderheid van een laboratorium-diamant wordt beoordeeld aan de hand van de gebreken, dat wil zeggen de insluitsels en onzuiverheden die de diamant zijn unieke karakter en charme geven. Ontdek hieronder meer over de helderheid van diamanten.
I.F.
Internally flawless (intern foutloos)
VVS 1
VVS 2
Very very slightly included (heel erg kleine inclusie)
VS 1
VS 2
Very slightly included (zeer geringe inclusie)
SI 1

SI 2

Slightly included (lichte inclusie)
I 1

I 2
I 3

Included (insluitsel)
Helderheidstabel voor diamanten
Title:Helderheidstabel en cijfers voor diamanten
Subtitle:
De helderheidstabel van diamanten loopt van I.F. tot I 3 en is gebaseerd op het aantal insluitsels en oneffenheden die in elke steen gevonden worden. De helderheidsgraad van diamanten wordt bepaald onder standaardomstandigheden met een vergroting van 10x. I.F. wordt gebruikt voor een intern foutloze diamant. Aan het andere uiteinde van de helderheidsschaal staat I 3 voor een zichtbare onzuiverheid. Echt foutloze diamanten zijn uiterst zeldzaam; bijna alle stenen, inclusief laboratorium-diamanten, hebben insluitsels van welke aard dan ook.
Kleurprincipes en -factoren
Title:
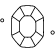
De kwaliteit van een laboratorium-diamant is gebaseerd op zijn grootte, symmetrie en glans. Een vakkundige slijpvorm creëert een veelheid aan facetten, die het licht absorberen en weerspiegelen zodat de steen vanuit elke hoek schittert.
Colorless
D-F
Near colorless
G-J
Slightly tinted
K-M
Very light color

N-R
Light color
S-Z
Diamond color scale and chart
Diamond coloring is rated on a scale from D to Z, with D clear ice white with no hint of yellow, while those rated Z are shades of yellow and brown. Each letter range on the chart denotes a shade of stone, with those rated D to F appearing colorless, through to S to Z appearing in shades of light yellow or brown. Swarovski only accepts the finest laboratory grown diamonds in its collections, meaning they range from colorless to nearly colorless diamonds (D-G).
Color Principles and Factors
Title:
Colorless stones are the most desirable in the world of diamonds and they are extremely rare. Swarovski Created Diamonds are evaluated against the standardized diamond color scale.

2.5 mm
0.05 CT

3.0 mm
0.10 CT

3.8 mm
0.20 CT

4.5 mm
0.30 CT

4.8 mm
0.40 CT

5.2 mm
0.50 CT

5.8 mm
0.70 CT

6.3 mm
0.90 CT

6.5 mm
1.00 CT

6.9 mm
1.25 CT
7.4 mm
1.50 CT
7.8 mm
1.75 CT
8.2 mm
2.00 CT
8.8 mm
2.50 CT
9.4 mm
3.00 CT
Diamond Carat Weight
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamond Carat Scale
Subtitle:
The carat measurement is derived by the word ‘carob’, a seed that was used as a diamond weight reference for traders in the ancient world. Carats are an international standard unit of measurement for the weight of a diamond. One carat is equal to 200 milligrams, so a 5 carat diamond will weigh one gram. The diamond carat does not refer to the size of a stone, simply how much it weighs. Diamonds usually become more expensive as their carat increases.
Discover Swarovski Created Diamonds
All About Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds
Subtitle:
Discover the world of Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry, redefining the future of diamonds with exceptional collections that bridge the gap between tradition and current trends. From the otherworldly brilliance of our interstellar collection to the pure elegance of our signature pieces, find a style that will last a lifetime.
Laboratory Grown Diamonds Buying Guide
Title:Find the perfect piece
Subtitle:
A natural progression of our brand DNA, Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry are laboratory grown diamonds, masterfully cut, intensely bright, and identical to their mined counterparts in every way but origin. Formed layer by layer from a carbon seed, they serve as a flawless reflection of nature’s radiance.
What are Laboratory Grown Diamonds?
Title:Laboratory Grown Diamonds explained
Subtitle:
Find out more about diamonds that are grown in a laboratory, and how the process of replicating the way diamonds are formed in the earth is achieved. Discover the different cuts of diamonds in the Swarovski Created Diamond Collections, as well as the inspiration behind the designs.
Foire aux questions
Les 4C du diamant - FAQ
Que signifient les 4C ?
Aucun diamant ne ressemble à un autre. Chaque pierre possède ses caractéristiques propres. Tout comme les diamants naturels, nos diamants créés en laboratoire sont évalués selon quatre critères appelés 4C. Reconnus dans le monde entier par l’industrie diamantaire, ces 4C interviennent dans le contrôle qualité du diamant et se réfèrent à la taille (cut), la clarté (clarity), la couleur (color) et le caratage (carat).
La clarté du diamant est-elle importante ?
Plus le degré de clarté est élevé, plus le diamant aura de la valeur, car il contiendra moins d’inclusions et d’imperfections.
Quel est le degré de clarté le plus élevé du diamant ?
La clarté dépend de la pureté de la pierre qui, elle-même, repose sur deux critères visuels : les inclusions et les imperfections.
Afin d’évaluer sa clarté, le diamant est inspecté à l’aide d’une loupe de grossissement 10x. Le nombre et la nature des éléments externes (imperfections) et internes (inclusions), ainsi que leur taille et leur position déterminent le degré de clarté.
Les pierres sont classées par les gemmologues de la meilleure note, IF (sans défaut interne), à la moins bonne, I3 (Inclusions).
Afin d’évaluer sa clarté, le diamant est inspecté à l’aide d’une loupe de grossissement 10x. Le nombre et la nature des éléments externes (imperfections) et internes (inclusions), ainsi que leur taille et leur position déterminent le degré de clarté.
Les pierres sont classées par les gemmologues de la meilleure note, IF (sans défaut interne), à la moins bonne, I3 (Inclusions).
Les diamants de laboratoire sont-ils sans défaut ?
Non, presque tous les diamants (extraits ou créés en laboratoire) contiennent des inclusions. Les inclusions métalliques ne concernent que les diamants de laboratoire. Si une trace de métal est détectée, on peut ainsi supposer qu’il s’agit d’un diamant de laboratoire. Bien que les diamants créés en laboratoire possèdent des défauts, Swarovski n’utilise que les pierres de la plus haute qualité dans ses collections Swarovski Created Diamond, certifiées par l’IGI (International Gemological Institute) et les 4C.
Les diamants de laboratoire peuvent-ils perdre leur éclat ?
Non, les diamants de laboratoire ne perdent rien de leur éclat avec le temps. Strictement identiques aux diamants naturels, ils sont dotés des mêmes caractéristiques physiques et chimiques. Leur apparence ne s’altère pas avec le temps. Lorsque le grain de carbone utilisé est de qualité inférieure, certains diamants peuvent contenir des défauts apparents, comme des problèmes de tonalités, des impuretés ou des altérations. Les bijoux Swarovski Created Diamonds ne contiennent aucun diamant aux défauts artificiels.
Comment se passe la certification et l’évaluation des diamants créés en laboratoire ?
Les diamants de laboratoire servant à la création des bijoux Swarovski Created Diamonds sont sélectionnés à la main et examinés par des experts gemmologues qui s’assurent de leur conformité aux normes de la plus haute qualité. Chaque pièce des collections Galaxy et Eternity est accompagnée d’un certificat numérique émis par l’IGI (International Gemological Institute).
Qu’appelle-t-on facette du diamant ?
Les facettes représentent les surfaces planes qui créent la forme du diamant. Chacun se dote de multiples facettes capables d’absorber et de refléter la lumière.
De quelle manière définit-on la qualité de la taille ?
Lorsqu’on parle de taille, on pense souvent à la silhouette de la pierre (ronde, cœur, ovale, marquise ou poire), alors qu’elle fait référence à la façon dont ses facettes interagissent avec la lumière. En réalité, la taille correspond à la mesure de la qualité des proportions géométriques, de la forme et de la finition du diamant. Les brillants seront notés sur une échelle allant de Idéal à Médiocre. Swarovski ne fait aucun compromis sur la qualité de la taille pour que chaque diamant créé en laboratoire diffuse un maximum de lumière et d’éclat.
Quelle est la meilleure taille de diamant ?
La taille fait référence aux différentes manières dont les facettes interagissent avec la lumière pour révéler le feu intérieur du diamant. C’est elle qui confère au diamant sa personnalité, tandis que l’attention apportée aux proportions, à la symétrie et aux facettes de nos Swarovski Created Diamonds sublimera leur brillance. La taille parfaite offre le juste équilibre entre largeur et profondeur, pour créer une symétrie : ni trop plat, ni trop profond. L’objectif étant de créer le point de réfraction parfait pour que la lumière circule à l’intérieur du diamant et soit réfléchie tout en mettant en valeur son éclat.
Comment déterminer la couleur d’un diamant ?
La couleur fait référence à la teinte naturelle du diamant blanc. L’usage est de comparer la couleur de chaque diamant avec un échantillon de référence, puis d’attribuer à celui-ci une lettre, allant de D (incolore) à Z (jaune pâle).
Plus le diamant est incolore, meilleure sera jugée la qualité.
Plus le diamant est incolore, meilleure sera jugée la qualité.
Les diamants de laboratoire ont-ils des imperfections ?
Lorsque le grain de carbone utilisé est de qualité inférieure, certains diamants peuvent contenir des défauts apparents, comme des problèmes de tonalités, des impuretés ou des altérations. Swarovski ne commercialise pas de diamants aux défauts artificiels.
Qu’est-ce que le caratage ?
Un carat désigne l’unité de poids spécifiquement adaptée aux pierres précieuses, dont font partie nos diamants créés en laboratoire. Un diamant pourra posséder un caratage plus élevé sans nécessairement être plus volumineux. De la même façon, le calibre de deux diamants de caratages identiques pourra varier selon la profondeur de la taille. Un carat pèse un 1/5ème de gramme et se divise en centièmes.
Qu’est-ce que le caratage du diamant ? A-t-il une importance et comment le mesurer ?
Le carat est l’unité de mesure standard du diamant et le premier critère d’évaluation pour déterminer la valeur de celui-ci. Le caratage mesure le poids du diamant. Chaque carat se divise en centièmes, permettant une mesure des plus précises. Un diamant de moins d’un carat sera exprimé en centièmes. Plus le diamant est gros, plus il contiendra de carats. Mais savoir si cela le rend précieux à vos yeux reste une question très personnelle.
Un caratage élevé est-il préférable ?
C’est une question très personnelle. Si vous souhaitez acquérir un gros diamant, le caratage aura alors son importance car du poids dépend la taille de celui-ci.