What Are the 4Cs of Diamonds?
หัวข้อ:
Universally recognized, the 4Cs are a guiding light in the world of diamonds, helping to determine the quality and value of each stone - the 4Cs stand for color, cut, carat, and clarity. The laboratory grown diamonds in the Swarovski Created Diamonds collections are graded against these 4Cs by IGI, the International Gemological Institute. The laboratory grown diamonds in these collections are of very fine quality: G+ in color and VS+ in clarity.
Clarity Principles and Factors
หัวข้อ:
The clarity of a laboratory grown diamond is judged by its flaws, which means the inclusions and blemishes that give it unique character and charm. Discover more about diamond clarity below.
I.F.
Internally flawless
VVS 1
VVS 2
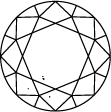
Very very slightly included
VS 1
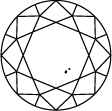
VS 2
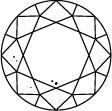
Very slightly included
SI 1

SI 2

Slightly included
I 1

I 2
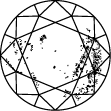
I 3

Included
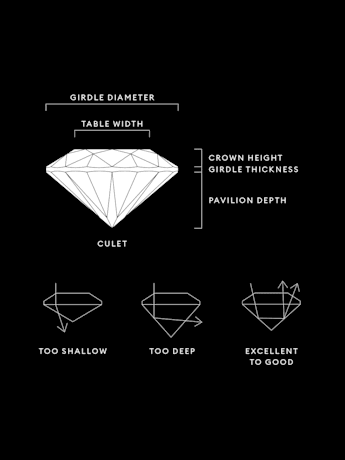
Diamond Clarity Chart
หัวข้อ:Diamond clarity scale and grades
หัวข้อย่อย:
The diamond clarity scale runs from I.F. to I 3 and is based on the number of inclusions and blemishes found in each stone. Diamond clarity grades are determined under standard viewing conditions with 10x magnification; I.F. is used to represent an internally flawless diamond, while at the other end of the diamond clarity chart, I 3 stands for the inclusion of a visible blemish. Truly flawless diamonds are extremely rare – almost all stones, including laboratory grown diamonds, have inclusions of some kind or other.
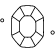
Cut Principles and Factors
หัวข้อ:
The quality of how a laboratory grown diamond is cut is based on its proportions, symmetry, and polish. An expert cut creates a multitude of facets, absorbing and reflecting the light so the stone shimmers from every angle.
Colorless
D-F
Near colorless
G-J
Slightly tinted
K-M
Very light color

N-R
Light color
S-Z
Diamond color scale and chart
Diamond coloring is rated on a scale from D to Z, with D clear ice white with no hint of yellow, while those rated Z are shades of yellow and brown. Each letter range on the chart denotes a shade of stone, with those rated D to F appearing colorless, through to S to Z appearing in shades of light yellow or brown. Swarovski only accepts the finest laboratory grown diamonds in its collections, meaning they range from colorless to nearly colorless diamonds (D-G).
Color Principles and Factors
หัวข้อ:
Colorless stones are the most desirable in the world of diamonds and they are extremely rare. Swarovski Created Diamonds are evaluated against the standardized diamond color scale.

2.5 mm
0.05 CT

3.0 mm
0.10 CT

3.8 mm
0.20 CT

4.5 mm
0.30 CT

4.8 mm
0.40 CT

5.2 mm
0.50 CT

5.8 mm
0.70 CT

6.3 mm
0.90 CT

6.5 mm
1.00 CT

6.9 mm
1.25 CT
7.4 mm
1.50 CT
7.8 mm
1.75 CT
8.2 mm
2.00 CT
8.8 mm
2.50 CT
9.4 mm
3.00 CT
Diamond Carat Weight
หัวข้อ:Laboratory Grown Diamond Carat Scale
หัวข้อย่อย:
The carat measurement is derived by the word ‘carob’, a seed that was used as a diamond weight reference for traders in the ancient world. Carats are an international standard unit of measurement for the weight of a diamond. One carat is equal to 200 milligrams, so a 5 carat diamond will weigh one gram. The diamond carat does not refer to the size of a stone, simply how much it weighs. Diamonds usually become more expensive as their carat increases.
Discover Swarovski Created Diamonds
All About Swarovski Created Diamonds
หัวข้อ:Laboratory Grown Diamonds
หัวข้อย่อย:
Discover the world of Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry, redefining the future of diamonds with exceptional collections that bridge the gap between tradition and current trends. From the otherworldly brilliance of our interstellar collection to the pure elegance of our signature pieces, find a style that will last a lifetime.
Laboratory Grown Diamonds Buying Guide
หัวข้อ:Find the perfect piece
หัวข้อย่อย:
A natural progression of our brand DNA, Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry are laboratory grown diamonds, masterfully cut, intensely bright, and identical to their mined counterparts in every way but origin. Formed layer by layer from a carbon seed, they serve as a flawless reflection of nature’s radiance.
What are Laboratory Grown Diamonds?
หัวข้อ:Laboratory Grown Diamonds explained
หัวข้อย่อย:
Find out more about diamonds that are grown in a laboratory, and how the process of replicating the way diamonds are formed in the earth is achieved. Discover the different cuts of diamonds in the Swarovski Created Diamond Collections, as well as the inspiration behind the designs.
Frequently asked questions
Diamond 4Cs FAQs
What are the 4Cs?
Every diamond varies slightly from the next and has its own individual distinguishing characteristics. Laboratory grown diamonds are 100% diamonds, and just like mined diamonds our laboratory grown diamonds are evaluated according to the 4Cs of diamond grading. The 4Cs are color, clarity, cut and carat weight, and they are the globally accepted standards used to assess the quality of diamonds.
Is diamond clarity important?
The higher the clarity grading, the less inclusions or blemishes a diamond has, making it a higher-value diamond than one with a lower grading.
What is the highest diamond clarity?
Diamond clarity is a measure of the purity of the stone graded by the visibility of two types of characteristics - inclusions and blemishes.
In order to assess clarity, the diamond is inspected under 10x power magnification. The number and nature of external (blemishes), and internal characteristics (inclusions), as well as their size and position, determine the grade.
Gemologists grade diamonds from Internally Flawless (IF) as the highest quality to Included (I3).
In order to assess clarity, the diamond is inspected under 10x power magnification. The number and nature of external (blemishes), and internal characteristics (inclusions), as well as their size and position, determine the grade.
Gemologists grade diamonds from Internally Flawless (IF) as the highest quality to Included (I3).
Are laboratory grown diamonds flawless?
No, nearly all diamonds (mined or laboratory grown) have inclusions. Metallic inclusions can occur in laboratory grown diamonds. If an expert spots a trace of metal in a diamond, they can assume it is laboratory grown. While laboratory grown diamonds with defects do exist, Swarovski only uses high quality laboratory grown diamonds certified by the International Gemological Institute (IGI) according to the 4Cs to ensure that only the finest quality diamonds join the Swarovski Created Diamond collections.
Do laboratory grown diamonds get cloudy?
No, laboratory-grown diamonds do not get cloudy over time. They are 100% identical to diamonds with the same physical and chemical properties, and should not degrade or change appearance over time. Where poor quality diamond seeds have been used, some laboratory-grown diamonds contain obvious defects, such as color tinges from impurities in the diamond or crystal structure imperfections. The laboratory grown diamonds processed in Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry are a very high quality standard and do not have unnatural, problematic characteristics.
How are laboratory grown diamonds certified and graded?
The laboratory grown diamonds processed in Swarovski Created Diamonds jewelry are hand-selected and examined by experienced gemologists to ensure they fulfill our high quality standards. Every piece of jewelry in the Galaxy and Eternity collections is accompanied with a digital laboratory report from the International Gemological Institute (IGI).
What are diamond facets?
Las facetas de un diamante son cada superficie facetada que crea la forma del diamante. Un diamante tiene varias facetas que absorben y reflejan la luz.
¿Cómo se determina la calidad de la talla de un diamante?
Generalmente, pensamos que la talla de un diamante hace referencia a su forma (redondo, ovalado, en corazón, marquesa, pera). Sin embargo, la talla del diamante significa lo bien que interactúan las facetas del diamante con la luz. La talla de un diamante es la medida de calidad de la forma, la geometría y el acabado del diamante. Los diamantes redondos brillantes reciben una calificación de talla oficial en una escala que va desde Ideal (el máximo) a Pobre. Swarovski se compromete con la calidad de la talla para garantizar que nuestros diamantes creados en laboratorio tienen un brillo y un reflejo de la luz inmejorables.
¿Cuál es la mejor talla de diamante?
La talla significa la manera en como las facetas del diamante interactúan con la luz para revelar un fuego interior. La talla aporta la personalidad al diamante. Con la mejora de las proporciones, la simetría y los ángulos de corte precisos, los Swarovski Created Diamonds ofrecen un brillo único. La mejor talla mantiene el equilibrio entre anchura y profundidad para crear una simetría ni demasiado superficial ni demasiado profunda. Se crea un punto de refracción perfecto de la luz a través del diamante, que a su vez se refleja dentro del diamante y potencia todo su brillo pulido.
¿Cómo se determina el color de un diamante?
El color hace referencia al tinte natural inherente de los diamantes blancos. El estándar industrial para calificar el color se basa en evaluar cada diamante respecto a un conjunto maestro y asignarle una letra de calificación de la D (incoloro) a la Z (amarillo suave).
Cuanto más incoloro sea el diamante, más calidad tendrá.
Cuanto más incoloro sea el diamante, más calidad tendrá.
¿Los diamantes creados en laboratorio tienen imperfecciones?
Si se utilizan semillas de diamante de mala calidad, los diamantes creados en laboratorio pueden contener defectos evidentes, como matices de color debidos a impurezas o imperfecciones estructurales. Swarovski no vende diamantes creados en laboratorio con características antinaturales y que puedan causar problemas.
¿Qué es el peso en quilates de un diamante?
Un quilate es una unidad de peso que se utiliza para medir piedras preciosas, incluidos los diamantes creados en laboratorio. Un diamante puede tener un mayor peso en quilates y no ser más grande, y dos diamantes con los mismos quilates pueden variar de medida si uno tiene una talla más profunda que el otro. Un quilate pesa 1/5 de un gramo y se divide en 100 puntos.
¿Qué es el peso en quilates de un diamante, cómo se mide y qué importancia tiene?
El peso en quilates es la unidad de peso estándar del diamante y el primer paso en el proceso de calificación. El peso en quilates de un diamante es la medida de peso de un diamante. Cada quilate se subdivide en 100 «puntos», lo que permite realizar mediciones precisas hasta la centésima parte. El peso de un diamante menor a un quilate puede describirse solo por sus «puntos». Cuanto más grande sea el diamante, más quilates pesará. Pero la importancia que tenga para ti, solo la decides tú.
¿Es mejor comprar un diamante con más quilates?
Es una cuestión muy personal. Si quieres un diamante más grande, busca un diamante con más quilates, ya que esto indica su peso y, por ende, su tamaño.