Quais são os 4Cs dos diamantes?
Title:
Universalmente reconhecidos, os 4Cs são uma luz orientadora no mundo dos diamantes, ajudando a determinar a qualidade e o valor de cada pedra - os 4Cs significam cor, corte, quilate e claridade. Os diamantes criados em laboratório nas coleções Swarovski Created Diamonds são avaliados com base nesses 4Cs pelo IGI, o Instituto Gemológico Internacional. Os diamantes criados em laboratório nestas coleções são de qualidade muito elevada: Cor G+ e clareza VS+.
Princípios e fatores de clareza
Title:
A clareza de um diamante cultivado em laboratório é julgada pelas suas falhas, ou seja, pelas suas inclusões e imperfeições que lhe conferem um caráter e charme únicos. Descubra mais sobre a clareza dos diamantes abaixo.
I.F.
Internamente irrepreensível
VVS 1
VVS 2
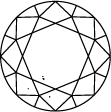
Inclusões muito, muito pequenas
VS 1
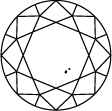
VS 2
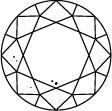
Inclusões muito pequenas
SI 1

SI 2

Inclusões pequenas
I 1

I 2
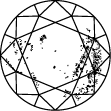
I 3

Inclusões
Tabela de clareza de diamantes
Title:Escala e graus de clareza de diamantes
Subtitle:
A escala de clareza de diamantes varia de I.F. a I 3 e é baseada no número de inclusões e imperfeições encontradas em cada pedra. Os graus de clareza dos diamantes são determinados sob condições de visualização padrão com ampliação de 10x; I.F. é usado para representar um diamante internamente irrepreensível, enquanto que no outro extremo da tabela de clareza de diamantes I 3 representa a inclusão de uma mancha visível. Diamantes verdadeiramente irrepreensíveis são extremamente raros, quase todas as pedras, incluindo os diamantes criados em laboratório, têm algum tipo de inclusão.
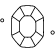
Princípios e fatores de corte
Title:
A qualidade de como um diamante criado em laboratório é lapidado baseia-se nas proporções, simetria e polimento. Um corte especializado cria uma infinidade de facetas, absorvendo e refletindo a luz para que a pedra brilhe de todos os ângulos.
Incolor
D-F
Quase incolor
G-J
Levemente com cor
K-M
Cor muito clara

N-R
Cor clara
S-Z
Escala e gráfico de cor dos diamantes
A coloração dos diamantes é classificada numa escala de D a Z, sendo D um branco gelo claro sem nenhum tom de amarelo, enquanto que os classificados como Z apresentam tons de amarelo e castanho. Cada faixa de letras no gráfico denota uma tonalidade da pedra, com os classificados de D a F a parecer incolores e os de S a Z em tons de amarelo claro ou castanho. A Swarovski só aceita os melhores diamantes criados em laboratório nas suas coleções, o que significa que variam de diamantes incolores a quase incolores (D-G).
Princípios e fatores de cor
Title:
As pedras incolores são as mais desejadas no mundo dos diamantes e são extremamente raras. Os Swarovski Created Diamonds são avaliados de acordo com a escala de cor padronizada de diamantes.

2,5 mm
0,05 CT

3,0 mm
0,10 CT

3,8 mm
0,20 CT

4,5 mm
0,30 CT

4,8 mm
0,40 CT

5,2 mm
0,50 CT

5,8 mm
0,70 CT

6,3 mm
0,90 CT

6,5 mm
1,00 CT

6,9 mm
1,25 CT
7,4 mm
1,50 CT
7,8 mm
1,75 CT
8,2 mm
2,00 CT
8,8 mm
2,50 CT
9,4 mm
3,00 CT
Peso do diamante em quilates
Title:Escala de quilates de diamantes criados em laboratório
Subtitle:
A medida em quilates é derivada da palavra “alfarroba”, uma semente que era usada como referência de peso para diamantes por comerciantes no mundo antigo. Quilates são uma unidade de medida padrão internacional para o peso de um diamante. Um quilate é igual a 200 miligramas. Assim, um diamante de 5 quilates pesa um grama. O quilate do diamante não se refere ao tamanho da pedra, mas apenas ao seu peso. Os diamantes geralmente tornam-se mais caros à medida que o quilate aumenta.
Descubra os Swarovski Created Diamonds
Saiba mais sobre os Swarovski Created Diamonds
Title:Diamantes criados em laboratório
Subtitle:
Descubra o mundo da joalheria Swarovski Created Diamonds, redefinindo o futuro dos diamantes com coleções excecionais que unem a tradição às tendências atuais. Do brilho sobrenatural da nossa coleção interestelar à pura elegância das nossas peças de assinatura, encontre um estilo que durará toda a vida.
Guia de compra para diamantes criados em laboratório
Title:Encontre a peça perfeita
Subtitle:
Uma progressão natural do ADN da nossa marca, a joalheria Swarovski Created Diamonds são diamantes criados em laboratório, lapidados com mestria, intensamente brilhantes e idênticos aos seus homólogos extraídos das minas em todos os aspetos salvo a origem. Formados camada a camada a partir de uma semente de carbono, servem como um reflexo perfeito do brilho da natureza.
O que são diamantes criados em laboratório?
Title:Diamantes criados em laboratório explicados
Subtitle:
Saiba mais sobre diamantes criados em laboratório e como o processo de replicar a forma como os diamantes são formados na terra é realizado. Descubra os diferentes cortes de diamantes das Coleções Swarovski Created Diamonds, bem como a inspiração por detrás dos designs.
Perguntas frequentes
Perguntas frequentes sobre os 4Cs dos diamantes
O que são os 4Cs?
Cada diamante é ligeiramente diferente do seguinte e possui as suas próprias características distintivas. Diamantes criados em laboratório são 100% diamantes e, assim como os diamantes extraídos, os nossos diamantes criados em laboratório são avaliados de acordo com os 4Cs da classificação de diamantes. Os 4Cs são cor, clareza, corte e peso em quilates, e são os padrões aceites globalmente para avaliar a qualidade dos diamantes.
A clareza do diamante é importante?
Quanto maior a classificação de clareza, menos inclusões ou imperfeições um diamante possui, tornando-o um diamante de maior valor do que outro com classificação inferior.
Qual é a maior clareza de diamante?
A clareza do diamante é uma medida da pureza da pedra, avaliada pela visibilidade de dois tipos de características – inclusões e imperfeições.
Para avaliar a clareza, o diamante é inspecionado sob uma ampliação de 10x. O número e a natureza das características externas (imperfeições) e internas (inclusões), bem como o seu tamanho e a sua posição, determinam o grau.
Os gemologistas classificam diamantes de Irrepreensível (IF) como a mais alta qualidade até Incluído (I3).
Para avaliar a clareza, o diamante é inspecionado sob uma ampliação de 10x. O número e a natureza das características externas (imperfeições) e internas (inclusões), bem como o seu tamanho e a sua posição, determinam o grau.
Os gemologistas classificam diamantes de Irrepreensível (IF) como a mais alta qualidade até Incluído (I3).
Os diamantes criados em laboratório são irrepreensíveis?
Não, quase todos os diamantes (extraídos ou cultivados em laboratório) têm inclusões. Podem ocorrer inclusões metálicas em diamantes criados em laboratório. Se um especialista detetar um traço de metal num diamante, pode assumir que é cultivado em laboratório. Embora existam diamantes criados em laboratório com defeitos, a Swarovski utiliza apenas diamantes criados em laboratório de alta qualidade, certificados pelo Instituto Gemológico Internacional (IGI) de acordo com os 4Cs, para garantir que apenas os diamantes da mais alta qualidade integram as coleções Swarovski Created Diamond.
Os diamantes criados em laboratório podem ficar opacos?
Não, os diamantes criados em laboratório não ficam opacos com o tempo. São 100% idênticos aos diamantes com as mesmas propriedades físicas e químicas e não devem degradar-se ou mudar de aparência ao longo do tempo. Quando são utilizadas sementes de diamante de má qualidade, alguns diamantes criados em laboratório apresentam defeitos evidentes, tais como tonalidades de cor resultantes de impurezas no diamante ou imperfeições na estrutura cristalina. Os diamantes criados em laboratório processados nas joias Swarovski Created Diamonds são de um padrão de qualidade muito elevado e não possuem características problemáticas não naturais.
Como são certificados e classificados estes diamantes?
Os diamantes criados em laboratório processados nas joias Swarovski Created Diamonds são selecionados manualmente e examinados por gemologistas experientes para garantir que cumprem os nossos elevados padrões de qualidade. Cada peça de joalheria das coleções Galaxy e Eternity é acompanhada por um relatório digital de laboratório do Instituto Gemológico Internacional (IGI).
O que são as facetas de um diamante?
As facetas de um diamante são cada superfície plana que cria a forma de um diamante. Todos os diamantes possuem múltiplas facetas que permitem absorver e refletir a luz.
Como é determinada a qualidade do corte do diamante?
Frequentemente pensamos no corte de um diamante enquanto forma (redondo, coração, oval, marquise, pera), mas o que o corte do diamante realmente significa é como as facetas de um diamante interagem com a luz. O corte de um diamante é a medida da qualidade da forma, geometria e acabamento do diamante. Os diamantes redondos brilhantes recebem uma classificação formal de corte numa escala de Ideal (o melhor) a Pobre. A Swarovski é inflexível quanto à qualidade do corte para garantir que todos os nossos diamantes criados em laboratório tenham desempenho de luz e brilho ideais.
Qual é o melhor corte de diamante?
Corte refere-se a como as facetas de um diamante interagem com a luz para revelar seu fogo interno. É o corte que confere a cada diamante a sua personalidade, e aperfeiçoar as proporções, simetria e ângulos de corte precisos dos diamantes criados em laboratório Swarovski Created Diamonds confere-lhes o seu brilho deslumbrante. O melhor corte tem um equilíbrio entre a largura e a profundidade para criar simetria, nem muito raso nem muito profundo. Criando o ponto de refração perfeito para a luz através do diamante, refletindo-a dentro do diamante e destacando o seu brilho polido.
Como é determinada a cor de um diamante?
A cor refere-se ao tom natural inerente dos diamantes brancos. O padrão da indústria para classificação de cor é avaliar cada diamante em comparação com um conjunto mestre e, em seguida, atribuir uma classificação de letra de D (incolor) a Z (amarelo claro).
Quanto mais próximo o diamante estiver de ser incolor, maior será a qualidade.
Quanto mais próximo o diamante estiver de ser incolor, maior será a qualidade.
Os diamantes criados em laboratório têm imperfeições?
Quando são utilizadas sementes de diamante de má qualidade, alguns diamantes criados em laboratório apresentam defeitos óbvios, tais como tonalidades de cor devido a impurezas ou imperfeições estruturais. A Swarovski não vende diamantes criados em laboratório com características problemáticas não naturais.
O que é o peso em quilates de um diamante?
Um quilate é uma unidade de peso usada especificamente para medir pedras preciosas, incluindo diamantes criados em laboratório. Um diamante pode ter um peso em quilates mais elevado sem parecer maior, e dois diamantes com o mesmo peso em quilates podem variar em tamanho se um for cortado mais profundamente do que o outro. Um quilate pesa 1/5 de um grama e é dividido em 100 pontos.
Quantos quilates tem um diamante, como é medido e quão importante é?
Os quilates são a unidade padrão de peso dos diamantes e o primeiro passo no processo de classificação. O peso em quilates do diamante é a medida de quanto o diamante pesa. Cada quilate pode ser subdividido em 100 "pontos". Isto permite medições precisas até à centésima casa decimal. O peso de um diamante com menos de um quilate pode ser descrito apenas pelos seus "pontos". Quanto maior for o diamante, mais quilates terá, mas apenas cada pessoa pode decidir quão importante isso é.
É melhor ter um diamante de quilate mais alto?
É uma questão totalmente pessoal. Se procura um diamante maior, deve procurar um quilate mais alto, já que isso indica o peso e, por conseguinte, o tamanho do diamante.